Introduction to Top Internal Controls for Fraud Prevention
- Top Internal Controls for Fraud Prevention: segregation of duties, regular audits and monitoring, strong authorization and approval policies, secure access controls, code of conduct, whistleblower policy, and employee training.
- Segregation of Duties: No single individual has complete authority over any critical business process.
- Regular Audits and Monoritoring: Ongoing oversight of organizational activities and serve as both detective and preventive controls.
- Strong Authorization and Approval Policies: Establish clear hierarchies and limits for financial commitments and operational decisions.
- Secure Access Controls: Preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems.
- Code of Conduct: Establishes the ethical foundation for organizational behavior
- Whistleblower Policy: Provides employees with safe channels to report suspected fraud, misconduct, or violations of organizational policies.
- Employee Training: Programs ensure that all staff members understand their roles in fraud prevention and can recognize potential fraud indicators.
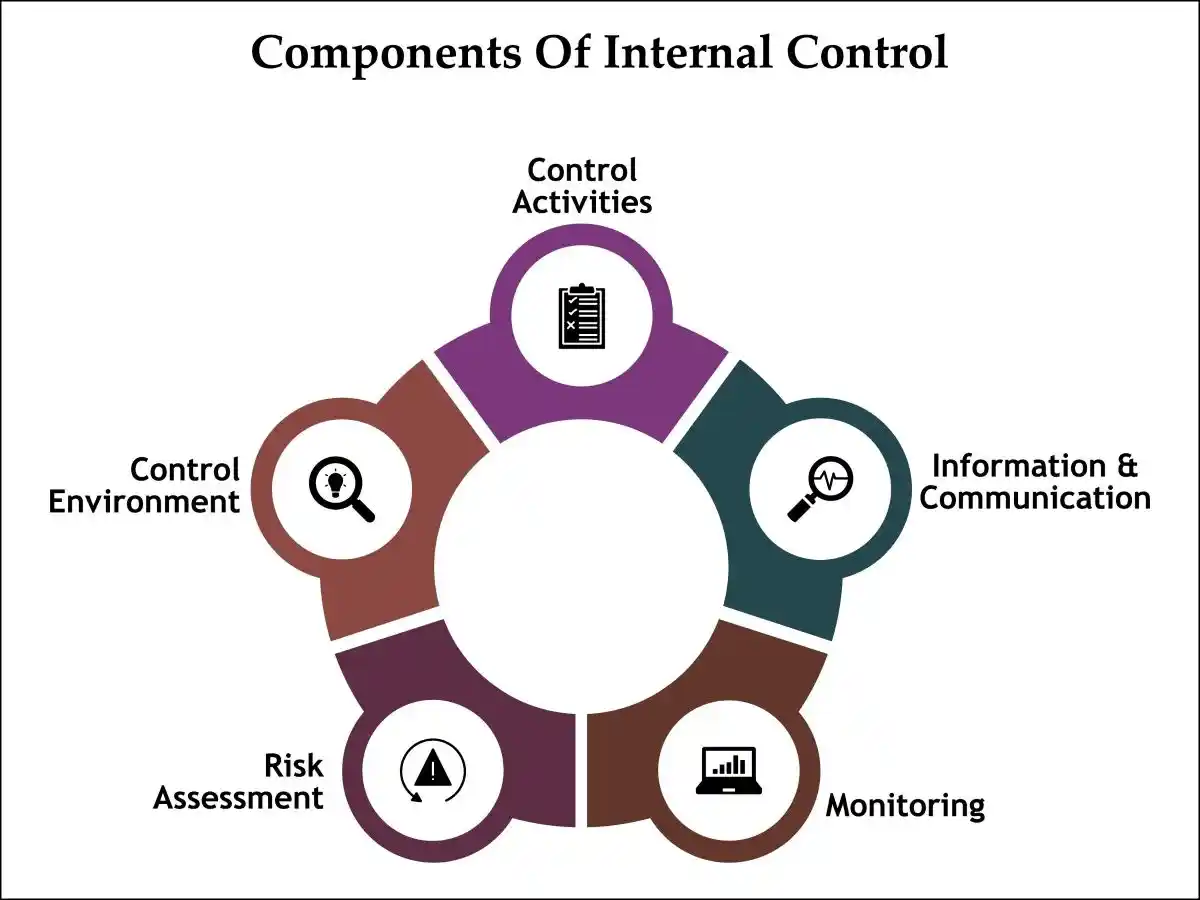
Understanding Internal Controls and Their Importance
Safeguarding Assets
- Internal controls: The processes, mechanisms, and procedures put in place by an organization to ensure the integrity of financial and accounting information, promote accountability, and prevent fraud.
- Protect Assets: These controls are designed to protect the organization’s assets from theft, fraud, and mismanagement.
- Digital Era: In an era where financial transactions are increasingly digital and sophisticated, the significance of robust internal controls cannot be overstated.
- First Line of Defense: They serve as the first line of defense against financial mishaps and fraudulent activities that could potentially cripple an organization.
Achieving Operational Efficiency
- Operational Efficiency: Beyond safeguarding assets, internal controls are crucial for achieving operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Streamline Processes: They help streamline processes, reduce waste, and ensure that the organization adheres to laws and regulations.
- Overall Performance: By ensuring that operations are carried out smoothly and that employees understand their roles and responsibilities, internal controls contribute to the organization’s overall performance and reputation.
- Competitive Advantage: A well-implemented internal control system can provide a competitive advantage by building trust with stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulators.
Fosture a Culture of Transparency and Accountability
- Transparency: Moreover, internal controls foster a culture of transparency and accountability within the organization.
- Clear Expectations: They set clear expectations for employee conduct and decision-making, which in turn helps deter unethical behavior.
- Integrity: By embedding these controls into the organization’s fabric, leaders can create an environment where honesty and integrity are valued.
- Mitigates Risk: This cultural shift not only helps in mitigating risks but also enhances employee morale and loyalty.
- Protection: Ultimately, by understanding and implementing effective internal controls, organizations can protect themselves from potential threats and pave the way for sustainable growth.

Top Internal Controls for Fraud Prevention
- Comprehensive: The most effective organizations implement comprehensive fraud prevention strategies that address vulnerabilities across all operational levels.
- Robust Framework: Top internal controls for fraud prevention form the backbone of any robust risk management framework, particularly in light of increasing regulatory enforcement actions and the rising threat of accounting fraud.
Segregation of Duties: The Foundation of Control
- Segregation of duties: Represents perhaps the most fundamental principle in fraud prevention and serves as the cornerstone of effective internal controls.
- Reduces Risk: This critical control mechanism ensures that no single individual has complete authority over any critical business process, creating a robust framework that significantly reduces the risk of accounting fraud and strengthens corporate governance across all organizational levels.
- Checkpoints: By dividing responsibilities among multiple employees, organizations create natural checkpoints that make fraudulent activities significantly more difficult to execute and conceal.
- Systematic Approach: To risk assessments and control implementation has become increasingly vital in today’s complex regulatory environment, where SEC enforcement actions continue to highlight the devastating consequences of inadequate internal control systems.
The Strategic Implementation of Segregation of Duties
Creating Layers of Verification
- Identify Coflicts: Effective segregation of duties requires comprehensive analysis of business processes to identify potential conflict points and vulnerabilities that could lead to securities class action lawsuits.
- Role Interaction: The implementation process demands careful consideration of how different roles interact within the organization’s operational framework, ensuring that regulatory compliance standards are met while maintaining operational efficiency.
- Segregation: For instance, the person who approves purchase orders should not be the same individual who receives goods or processes vendor payments.
- Multiple Layers: This fundamental separation creates multiple layers of verification that serve as powerful deterrents against fraudulent schemes.
Clearly Defined Responsibilities
- Boundries: Similarly, employees responsible for recording transactions should not have access to the underlying assets, establishing clear boundaries that prevent unauthorized manipulation of financial records.
- Encompases all Aspects: The principle extends beyond basic transaction processing to encompass all aspects of corporate governance.
- Distinct Responsibilities: Organizations must ensure that those who initiate transactions, those who authorize them, those who record them, and those who maintain custody of related assets represent distinct individuals with clearly defined responsibilities.
- Checks and Balances: This comprehensive approach to internal controls creates a system of checks and balances that serves as a powerful deterrent against accounting fraud.
Integration with Comprehensive Internal Control Systems
Most Effective when Integrated with Other Controls
- Segregation of duties: Works most effectively when integrated with other top internal controls for fraud prevention.
- Regular audits and monitoring: Provides ongoing verification that segregation principles remain intact and effective.
- Ensure Proper Seperation: These audits should examine not only the formal organizational structure but also the actual day-to-day operations to ensure that duties remain properly separated in practice.
Created Hierarchies of Approval Process
- Strong authorization and approval policies: Complements segregation of duties by establishing clear hierarchies and approval thresholds.
- Additional Control Layer: These policies must specify who can authorize different types of transactions and under what circumstances, creating additional layers of control that prevent unauthorized activities.
- Signifcant Fraud Reduction: The combination of proper segregation and robust authorization frameworks significantly reduces opportunities for fraudulent manipulation.
Works Synergistically with Secure Access Controls
- Secure access controls: Represents another critical component that works synergistically with segregation of duties.
- Limiting Access: By implementing sophisticated access management systems, organizations can ensure that employees can only access the systems and information necessary for their specific roles.
- Hollistic Approach: This technological enforcement of segregation principles provides additional protection against both intentional fraud and inadvertent errors.
Regular Audits and Monitoring: Continuous Vigilance
- Regular audits and monitoring: Provides ongoing oversight of organizational activities and serve as both detective and preventive controls.
- Systematic Approach: These processes involve systematic examination of financial records, operational procedures, and compliance with established policies.
- Modern audit functions: Extends beyond traditional financial audits to include operational audits, compliance audits, and fraud-specific examinations.
- Effectiveness of Audit Programs: Depends on their frequency, scope, and independence.
- Internal Audit Teams: Should report directly to the audit committee of the board of directors, ensuring their independence from operational management.
- Surprise Audits and Continuous Monitoring: Technologies can help identify anomalies in real-time, enabling rapid response to potential fraud indicators.
The Evolution of Modern Audit Functions
- Contemporary Audit Programs: Have evolved far beyond traditional financial examinations.
- Comprehensive Approach: Encompasses operational audits, compliance audits, and specialized fraud-specific examinations that work together to create multiple layers of protection.
- Multi-Faceted Approach: Is particularly crucial given the increasing complexity of securities litigation and the heightened scrutiny from regulatory bodies.
- Financial audits: Remain the foundation, systematically examining accounting records and financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with established standards.
- Operational Audits: Have become equally important, evaluating the effectiveness of business processes and identifying potential vulnerabilities that could lead to fraudulent activities.
Independence: The Critical Success Factor
- Independence: The effectiveness of any audit program fundamentally depends on independence from operational management.
- Strong Authorization and Approval Policies: Require that internal audit teams report directly to the audit committee of the board of directors, ensuring their objectivity remains uncompromised.
- Integrity: This independence is not merely procedural—it’s essential for maintaining the integrity that prevents conflicts of interest and ensures unbiased evaluation of organizational activities.
- Must Retain Independence: When audit functions lack independence, they become ineffective at detecting fraud schemes that may involve senior management.
- Regulatory Compliance: This independence requirement has become even more critical following numerous SEC enforcement actions that have highlighted the consequences of compromised audit oversight.
Technology-Enhanced Continuous Monitoring
- Modern Technology: Modern secure access controls and advanced monitoring technologies have revolutionized traditional audit approaches.
- Continuous Monitoring Pystems: Now enable real-time detection of anomalies, allowing organizations to identify potential fraud indicators immediately rather than waiting for periodic audit cycles.
- Flag Inconsistent Patters: These technological solutions can automatically flag unusual transactions, identify patterns consistent with fraudulent activity, and provide instant alerts when predetermined risk thresholds are exceeded.
- Proactivly Preventing Fraud: This capability is particularly valuable for preventing accounting fraud schemes that might otherwise go undetected for extended periods.
Integration with Comprehensive Risk Assessments
- Effective Audit Programs: Must be integrated with broader risk assessments to ensure comprehensive coverage of potential fraud vulnerabilities.
- Focus on High Risk: This integration ensures that audit activities focus on areas of highest risk while maintaining appropriate coverage across all organizational functions.
- Risk assessments: Informes audit planning by identifying emerging threats, evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls, and prioritizing audit resources where they can provide maximum value.
- Strategic Approach: Ensures that limited audit resources are deployed most effectively.
Strong Authorization and Approval Policies
- Strong authorization and approval policies: establish clear hierarchies and limits for financial commitments and operational decisions.
- Defines Authorization: These policies define who can authorize various types of transactions, establish spending limits at different organizational levels, and require multiple approvals for significant expenditures or unusual transactions.
- Effective authorization: Controls include written policies that clearly define approval authorities, mandatory documentation requirements for all approvals, and regular review of authorization limits to ensure they remain appropriate.
- Preventing Circumvention: Organizations must also implement controls to prevent the circumvention of approval processes and ensure that all transactions are properly authorized before execution.
The Strategic Importance of Authorization Controls
- Robust Authorization: In today’s complex business environment, where securities litigation and regulatory enforcement actions continue to rise, robust authorization policies serve as the first line of defense against fraudulent activities.
- Defining Authhorization: These controls define who can authorize various types of transactions, establish spending limits at different organizational levels, and require multiple approvals for significant expenditures or unusual transactions.
- Improper Authorization: The absence of proper authorization controls has been a contributing factor in numerous high-profile corporate scandals that resulted in securities class actions and substantial investor losses.
- Regulary Enforcment: When companies fail to implement adequate approval mechanisms, they create environments where unauthorized transactions can occur, financial statements can be manipulated, and regulatory compliance requirements can be violated.

Essential Components of Effective Authorization Policies
- Written Policies with Clear Definition of Approval Authorities: Effective authorization controls begin with comprehensive written policies that clearly define approval authorities at every organizational level. These policies must specify dollar thresholds, transaction types, and the specific individuals or positions authorized to approve different categories of expenditures and commitments.
- Mandatory Documentation Requirements: All approvals must be properly documented, creating an audit trail that supports regular audits and monitoring activities.
- Transparency: This documentation serves as evidence that proper procedures were followed and provides transparency for both internal oversight and external regulatory review.
- Hierarchical Approval Structure: Organizations must implement a tiered approval system where larger transactions require higher-level authorization. This segregation of duties ensures that no single individual has excessive control over financial decisions and creates natural checkpoints in the approval process.
- Regular Review and Updates: Authorization limits and approval authorities must be reviewed regularly to ensure they remain appropriate for current business conditions and organizational structure. This ongoing assessment is crucial for maintaining effective internal controls as companies grow and evolve.
Integration with Risk Assessment and Corporate Governance
- Strong Authorization Policies: cannot operate in isolation but must be integrated with comprehensive risk assessmentsand broader corporate governance initiatives.
- Framework Revaluation: Organizations should rregularly evaluate their authorization frameworks against identified risks, ensuring that approval requirements are commensurate with potential exposure.
- Regulatory Compliance: The connection between authorization controls and corporate governance is particularly important in light of increasing regulatory compliance requirements.
- Protect Shareholders: Companies must demonstrate to regulators, auditors, and stakeholders that they have implemented appropriate controls to prevent unauthorized transactions and protect shareholder interests.
Integration with Risk Assessment and Corporate Governance
Strong authorization policies cannot operate in isolation but must be integrated with comprehensive risk assessments and broader corporate governance initiatives. Organizations should regularly evaluate their authorization frameworks against identified risks, ensuring that approval requirements are commensurate with potential exposure.
The connection between authorization controls and corporate governance is particularly important in light of increasing regulatory compliance requirements. Companies must demonstrate to regulators, auditors, and stakeholders that they have implemented appropriate controls to prevent unauthorized transactions and protect shareholder interests.
Implementation Best Practices
- Establish Clear Dollar Thresholds: Organizations should implement specific dollar amounts that trigger different levels of approval.
- For example, department managers might authorize expenditures up to $5,000, while amounts exceeding $50,000 require executive approval, and transactions over $500,000 need board authorization.
- Implement Technology Solutions: Modern authorization systems should leverage technology to enforce approval workflows, maintain documentation, and provide real-time monitoring capabilities.
- These systems can automatically route transactions to appropriate approvers and maintain comprehensive audit trails.
- Create Exception Handling Procedures: While maintaining strict controls, organizations must also establish procedures for handling llegitimate emergency situations that may require expedited approvals.
- These exception processes should include additional documentation requirements and post-approval review procedures.
- Training and Communication: All employees must understand the authorization policies and their role in maintaining effective controls.
- Regular training programs should emphasize the importance of these controls in preventing fraud and protecting the organization from legal and financial risks.
Secure Access Controls: Protecting Digital Assets
- Strong authorization and approval policies: Serve as the backbone of effective internal controls and represent one of the most critical components in preventing fraudulent activities.
- Reduce Risk Exposure: These policies establish clear hierarchical approval structures that ensure no single individual can authorize transactions or make decisions that could expose the organization to significant financial risk.
Multi-Level Approval Frameworks
- Effective Authorization Policies: Implements segregation of duties by requiring multiple levels of approval for financial transactions, contract modifications, and system access changes.
- Purchase Orders: Those exceeding predetermined thresholds must receive approval from department managers, finance directors, and executive leadership, depending on the transaction value.
- Layered Approach: Prevents any single employee from initiating, processing, and recording transactions independently.
Digital Authorization Systems
- Modern Authorization Frameworks: Leverage technology to create audit trails and eenforce approval workflows automatically.
- Digital Signature Systems: Electronic approval workflows, and automated spending controls ensure that all transactions follow established protocols while maintaining comprehensive documentation for regulatory compliance purposes.
Risk-Based Approval Thresholds
- Risk Based Approval: Organizations must establish risk-based approval thresholds that align with their risk assessments and operational requirements.
- Routine Transactions: Low-risk, routine transactions may require minimal approval, while high-value or unusual transactions demand extensive review and authorization from senior management.
- Regulatory Compliance: These thresholds should be regularly reviewed and adjusted based on changing business conditions and regulatory requirements.
Vendor and Third-Party Authorization Controls
- Strong Authorization Policies: Extend beyond internal transactions to include ccomprehensive controls over vendor relationships, contract approvals, and third-party access to organizational systems.
- Prevent Unauthorized Transactions: These controls help prevent fraudulent schemes involving fictitious vendors, unauthorized contract modifications, or iinappropriate third-party access to sensitive information.
The Human Element in Fraud Prevention
While technical controls are essential, the human element remains critical in fraud prevention efforts. Organizations must address behavioral factors and create an environment that discourages fraudulent activities while encouraging ethical conduct.
Code of Conduct: Setting Ethical Standards
- Comprehensive Code of Conduct: Establishes the ethical foundation for organizational behavior, serving as the cornerstone of effective corporate governance and regulatory compliance.
- Defines Company’s Values: This document must clearly articulates the organization’s values, define acceptable and unacceptable behaviors, and provide guidance for ethical decision-making.
- Conflicts of Interests: The code must address conflicts of interest, proper use of organizational resources, confidentiality requirements, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- More Than Documentation: However, effective codes of conduct require more than mere documentation.
- Empliment Employee Training: Organizations must actively communicate these standards through comprehensive employee training programs, regular reminders, and consistent enforcement.
- Leadership Commitment to Ethical Behavior: Sets the tone at the top and demonstrates the organization’s serious commitment to integrity, particularly in preventing accounting fraud and mitigating risks associated with securities class action lawsuits.
Strong Authorization and Approval Policies: The Foundation of Fraud Prevention
- Strong Approval Policies: Among the top internal controls for fraud prevention, strong authorization and approval policies represent perhaps the most critical safeguard against financial misconduct and operational irregularities.
- Hierarchical Structures: These policies establish clear hierarchical structures for decision-making, ensuring that no single individual can initiate, authorize, and ccomplete transactions without appropriate oversight.
Whistleblower Policy: Encouraging Reporting
Employee Reporting Protections: A robust whistleblower policy provides employees with safe channels to report suspected fraud, misconduct, or violations of organizational policies.
Whistleblower Protections: These policies must guarantee protection against retaliation and offer multiple reporting mechanisms, including anonymous options, to accommodate different comfort levels and circumstances.
Clear Communication Channels: Successful whistleblower programs require clear communication about available reporting channels, prompt investigation of reported concerns, and feedback to reporters when appropriate.
Regulary Assess Effectiveness: Organizations should regularly assess the effectiveness of their whistleblower programs and make necessary improvements to encourage reporting and maintain employee confidence in the process.
Documentation and Audit Trail Requirements
- Strong Authorization and Approval Policies: Mandate comprehensive documentation for every approval decision.
- Expenditure Documentation: This includes written justification for expenditures, supporting documentation such as contracts or invoices, and clear identification of the approving authority.
- Digital Approval Systems: Should maintain immutable audit trails, recording timestamps, user identifications, and approval rationales.
- Identify Control Weaknesses: These documentation requirements prove invaluable during regular audits and monitoring activities, enabling auditors to reconstruct decision-making processes and identify potential control weaknesses.
- Protection for Regulatory Enforcment: The audit trail also serves as crucial evidence in regulatory enforcement proceedings or securities litigation scenarios.
Employee Training: Building Awareness and Capability
- Comprehensive Employee Training Programs: ensure that all staff members understand their roles in fraud prevention and can recognize potential fraud indicators.
- Training Protocal: Training should cover the organization’s internal controls, ethical standards, reporting procedures, and specific fraud risks relevant to each employee’s position.
- Effective Training Programs: Use varied delivery methods, provide rregular updates on emerging fraud trends, and include practical scenarios that help employees apply their knowledge.
- Specialized Training: Organizations should also provide specialized training for employees in high-risk positions and ensure that new employees receive fraud awareness training as part of their orientation process.
Regulatory Compliance and Corporate Governance
The regulatory landscape surrounding corporate governance and fraud prevention continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on proactive risk management and transparent reporting. Organizations must stay current with regulatory requirements and enforcement trends to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties.
SEC Enforcement Actions: Learning from Regulatory Responses
- Recent SEC enforcement Actions: Provide valuable insights into regulatory priorities and expectations for internal controls.
- Focus on Iadequate Controls: The SEC has increasingly focused on cases involving inadequate internal controls, particularly those that failed to prevent or detect accounting fraud.
- Expectations: These actions demonstrate the regulator’s expectation that organizations maintain robust control environments and take prompt corrective action when deficiencies are identified.
- Litigation: Securities class action lawsuits and securities litigation often follow significant control failures, highlighting the financial and reputational consequences of inadequate fraud prevention measures.
- Deficient Controls Leads to Litigation: Organizations facing securities class actions frequently cite internal control deficiencies as contributing factors to the underlying problems that led to litigation.
Regulatory Compliance Framework
Effective Regulatory Compliance: Requires a comprehensive framework that addresses applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
Regular Compliance Assessments: This framework should include regular compliance assessments, monitoring of regulatory changes, and prompt implementation of necessary updates to policies and procedures.
Operational and Complaince Risks: Organizations must also consider the intersection between fraud prevention and regulatory compliance, ensuring that internal controls address both operational risks and compliance requirements.
Integrated Approach: Helps prevent situations where compliance failures create opportunities for fraudulent activities.
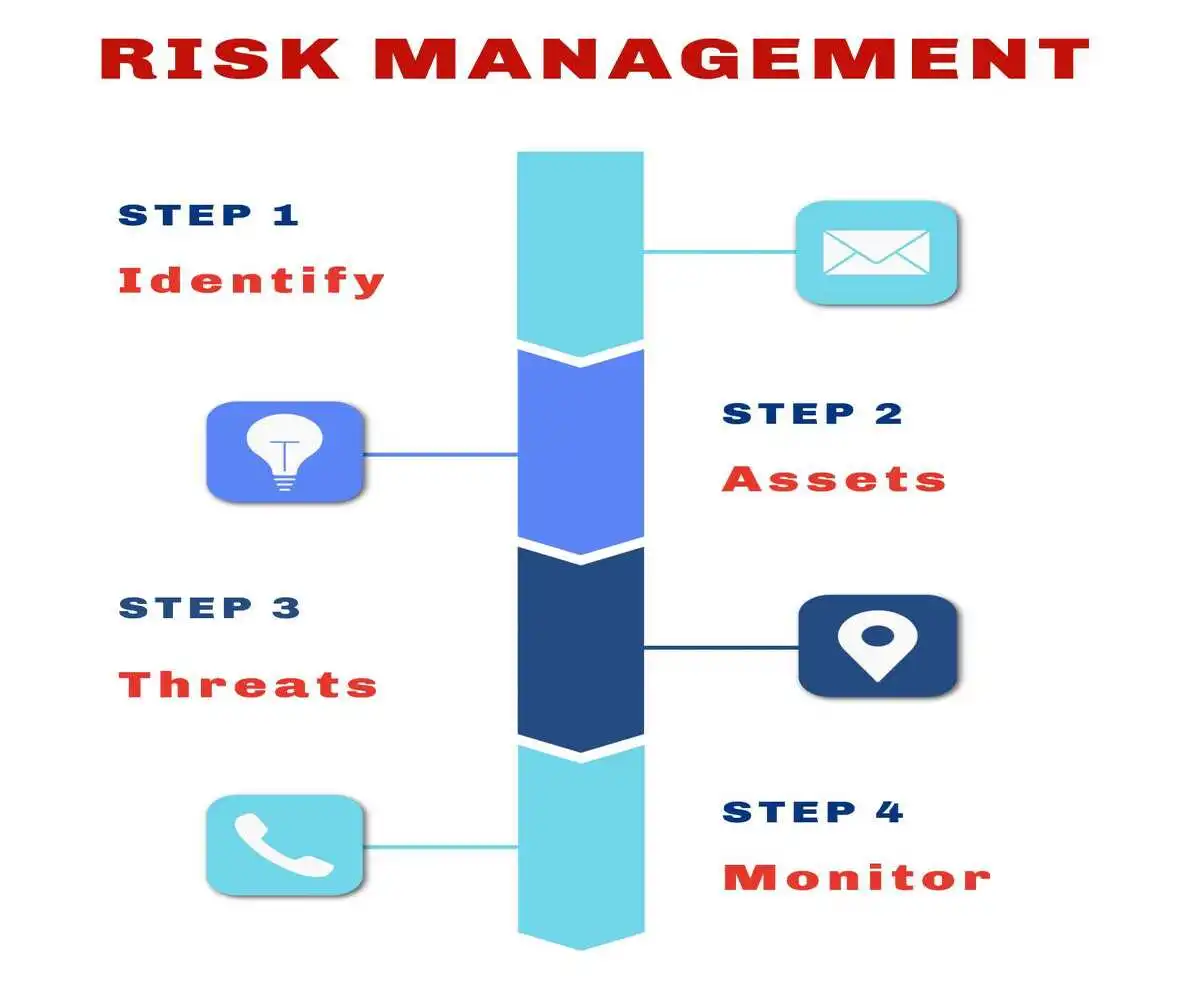
Risk Assessments: The Strategic Foundation
Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Form the strategic foundation for effective internal controls and fraud prevention programs.
Identify Vulnerabilities: These assessments identify potential vulnerabilities, evaluate the likelihood and impact of various fraud scenarios, and guide the allocation of resources to address the most significant risks.
Effective Risk Assessment Processes: Consider both internal and external factors that could create fraud opportunities. Internal factors include organizational structure, employee turnover, compensation structures, and operational pressures.
External Factors: Encompass industry trends, economic conditions, regulatory changes, and competitive pressures.
Risk Assessments: Should be conducted regularly and updated whenever significant changes occur in the organization or its operating environment.
Building a Comprehensive Control Environment
Complete Integration: The most effective fraud prevention strategies integrate all these elements into a comprehensive control environment that addresses technical, procedural, and cultural factors.
Holistic Approach: Recognizes that fraud prevention requires more than individual controls—it demands a coordinated system that reinforces ethical behavior and makes fraudulent activities both difficult to execute and likely to be detected.
Regular Evaluations: Organizations must regularly evaluate the effectiveness of their control environments, making necessary adjustments to address emerging risks and changing business conditions.
Ongoing Assessment and Improvement Process: Ensures that internal controls remain relevant and effective in preventing fraud and protecting organizational assets.
Reduced Exposure: By implementing these top internal controls for fraud prevention and maintaining a strong commitment to ethical conduct, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to fraud risks while building stakeholder confidence in their governance and risk management capabilities.
Improved Operational Efficiency: The investment in comprehensive internal controls pays dividends through reduced fraud losses, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced reputation in the marketplace.
Conclusion: Building a Culture of Integrity and Accountability
Building A Culture of Integrity and Accountability: is the cornerstone of effective fraud prevention.
Fostering an Ethical Environment: Where ethical behavior is valued and rewarded, organizations can deter fraudulent activities and protect their assets.
Tone at the Top Culture: This culture begins with leadership, as management sets the tone for the organization and serves as a role model for employees. Leaders must demonstrate a commitment to ethical conduct and ensure that internal controls are prioritized and enforced.
Creating a Culture of Integrity: Involves more than just implementing internal controls; it requires a holistic approach that includes clear communication, ongoing training, and employee engagement.
Promote Open Dialouge: Organizations should promote open dialogue about ethical behavior and encourage employees to speak up if they suspect fraud or misconduct. By providing support and resources for employees, organizations can empower them to act with integrity and accountability.
A Culture of Integrity: Ultimately, building a culture of integrity and accountability is an ongoing process that requires dedication and commitment from all levels of the organization.
Ethical Behavior: By prioritizing ethical behavior and implementing strong internal controls, organizations can create a resilient framework that not only prevents fraud but also enhances their reputation and long-term success.
Culture of Integrity: In a world where fraud threats continue to evolve, a culture of integrity remains the most effective defense against internal and external challenges.
Contact Timothy L. Miles Today for a Free Case Evaluation
If you suffered substantial losses and wish to serve as lead plaintiff in a securities class action, or have questions about securities class action settlements, or just general questions about your rights as a shareholder, please contact attorney Timothy L. Miles of the Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles, at no cost, by calling 855/846-6529 or via e-mail at [email protected]. (24/7/365).
Timothy L. Miles, Esq.
Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles
Tapestry at Brentwood Town Center
300 Centerview Dr. #247
Mailbox #1091
Brentwood,TN 37027
Phone: (855) Tim-MLaw (855-846-6529)
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.classactionlawyertn.com
Facebook Linkedin Pinterest youtube
Visit Our Extensive Investor Hub: Learning for Informed Investors