Key Principals of Corporate Governance: A Comprehensive Framework for Modern Business Excellence
- Key principles in corporate governance represents far more than a regulatory checkbox—it serves as the foundational architecture that determines how companies operate, compete, and create sustainable value in today’s complex global marketplace.
- This framework of rules, practices, and processes fundamentally shapes how organizations direct their operations while balancing the diverse interests of shareholders, management, customers, suppliers, financiers, government entities, and broader communities.
The Strategic Foundation of Modern Governance
- At its essence, corporate governance ensures accountability and transparency in every stakeholder relationship, fostering the trust that enables long-term sustainability.
- Consider the transformation of Microsoft under Satya Nadella’s leadership—when he assumed the CEO role in 2014, the company implemented enhanced governance practices that emphasized transparency in decision-making and stakeholder engagement.
- This governance evolution contributed significantly to Microsoft’s market capitalization growing from approximately $300 billion to over $2 trillion.
- The increasing complexity of global markets and heightened regulatory scrutiny have made robust governance frameworks indispensable for companies striving to maintain integrity and competitiveness.
- Research cited by Bloomberg found that over a two-year period, the top fifth of corporate governance performers in the S&P 500 index outperformed the bottom fifth by 15%
Core Components of Effective Governance
Effective corporate governance encompasses several critical elements:
- Board Composition and Independence: Ensuring diverse expertise and independent oversight
- Executive Compensation Alignment: Linking leadership rewards to long-term performance metrics
- Risk Management Protocols: Implementing comprehensive systems to identify and mitigate potential threats
- Stakeholder Communication: Maintaining transparent, regular dialogue with all interested parties
- Ethical Standards Enforcement: Establishing clear guidelines and accountability mechanisms
The overarching goal remains aligning the interests of individuals, corporations, and society as closely as possible.
- When Patagonia implemented its “1% for the Planet” initiative alongside enhanced governance structures, the company demonstrated how strong governance can drive both profitability and social responsibility—resulting in consistent revenue growth while maintaining industry-leading employee satisfaction scores.
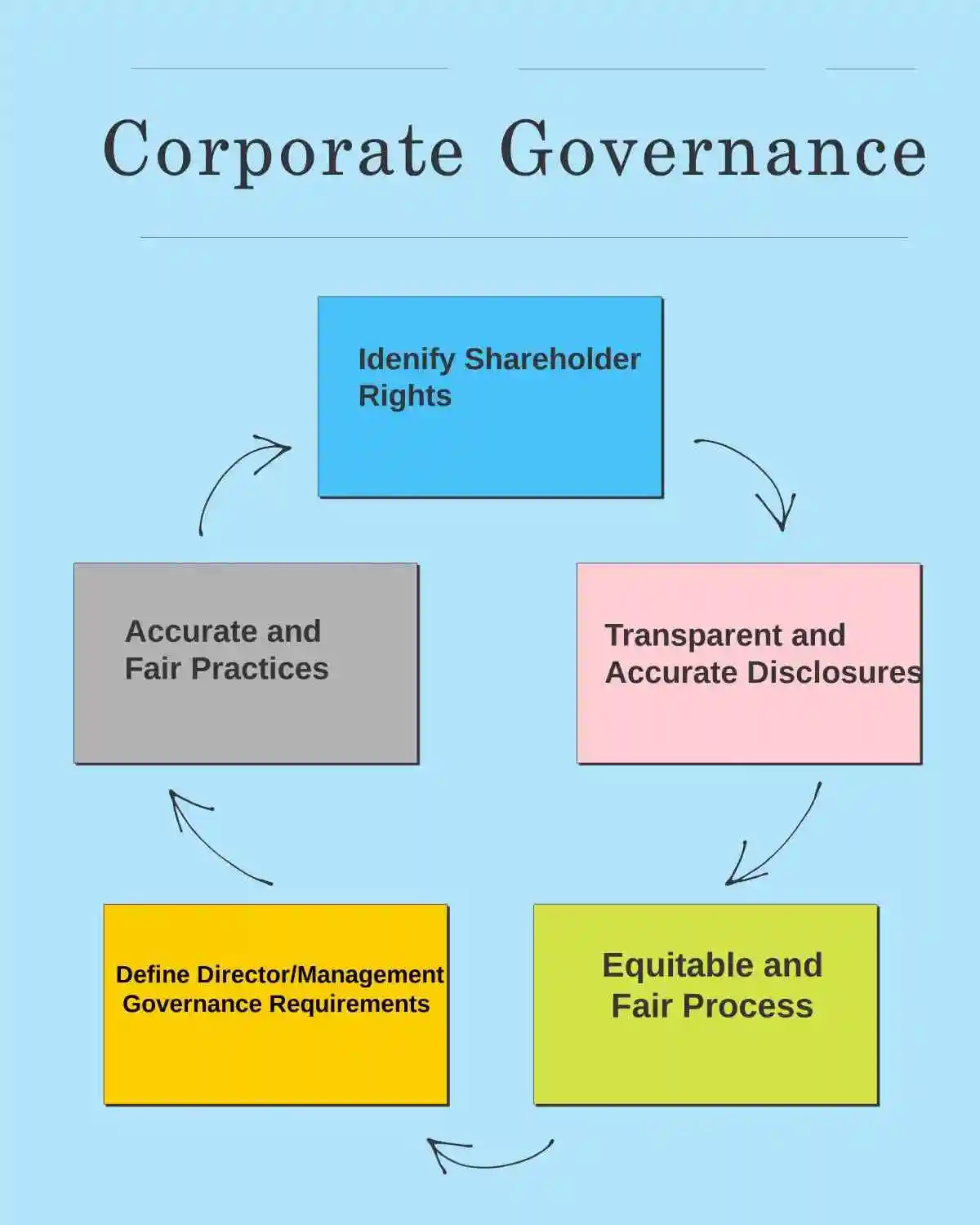
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE BEST PRACTICES PRINCIPLES CHART
Recent Developments Reshaping Governance Landscapes
The governance landscape has experienced significant evolution, particularly following high-profile corporate scandals and the 2008 financial crisis. Recent regulatory developments include:
- The implementation of enhanced cybersecurity disclosure requirements by the SEC in 2023
- Increased focus on climate-related financial disclosures following international agreements
- Strengthened requirements for board diversity and inclusion reporting
- Enhanced scrutiny of executive compensation packages and their performance linkages
Economic Implications and Market Impact
- The economic implications of strong corporate governance extend far beyond individual companies.
- Research from McKinsey & Company demonstrates that countries with robust governance frameworks attract 25% more foreign direct investment than those with weaker systems.
- This correlation highlights governance’s role in creating stable, attractive business environments.
- From a market perspective, governance quality directly impacts:
- Capital Access: Well-governed companies typically secure financing at lower costs
- Valuation Premiums: Strong governance can add to company valuations
- Risk Mitigation: Effective oversight reduces operational and reputational risks
- Innovation Capacity: Transparent decision-making processes often foster more innovative cultures
- The 2022 collapse of FTX serves as a stark reminder of governance failures’ consequences—the cryptocurrency exchange’s lack of proper oversight mechanisms and transparency led to billions in investor losses and widespread market disruption.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Integration
- As companies face mounting pressure to demonstrate commitment to ESG criteria, corporate governance has become the critical framework for integrating these considerations into business strategy.
- The role of governance in shaping corporate culture and values has never been more critical, with investors increasingly viewing governance quality as predictive of long-term performance.
- Companies like Unilever have demonstrated how strong governance can drive ESG integration—their Sustainable Living Plan, Fraud on the Market Theory in Securities Litigation: A Step-By-Step Panoramic Investor Playbook [2025], has contributed to consistent outperformance of market benchmarks while achieving significant environmental and social impact goals.
Building Sustainable Competitive Advantage
- Corporate governance helps companies build goodwill and maintain investor confidence, which proves crucial for securing capital in competitive markets.
- It mitigates risks by ensuring ethical behavior and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements while establishing clear lines of authority and accountability.
- By preventing conflicts of interest and fostering ethical decision-making at all organizational levels, effective governance creates sustainable competitive advantages.
- As global markets continue evolving and stakeholder expectations rise, companies that prioritize governance excellence position themselves for long-term success while contributing to broader economic stability and social progress.
- The future belongs to organizations that view corporate governance not as a compliance burden, but as a strategic enabler of sustainable growth, innovation, and stakeholder value creation.
The Evolution and Impact of Corporate Governance Principles: A Comprehensive Framework for Modern Business Excellence
- Corporate governance has emerged as the cornerstone of sustainable business success in today’s interconnected global economy.
- The foundation of effective corporate governance lies in a set of core principles that guide the behavior and decision-making of corporations, creating a robust framework that extends far beyond mere regulatory compliance.
Accountability: The Bedrock of Corporate Trust
- Accountability serves as the fundamental pillar upon which all other governance principles rest.
- This principle ensures that individuals and groups within organizations are held responsible for their actions and decisions, creating a culture of ownership and responsibility.
- Consider the transformative case of Microsoft under Satya Nadella’s leadership.
- When Nadella became CEO in 2014, he implemented radical accountability measures that revolutionized the company’s culture.
- Department heads were required to present quarterly accountability reports directly to the board, detailing not just successes but also failures and lessons learned. This approach led to:
- Enhanced stakeholder confidence through transparent reporting mechanisms
- Improved decision-making processes with clear ownership structures
- Reduced operational risks through proactive identification of potential issues
- Strengthened regulatory compliance via systematic oversight protocols
- The economic implications of robust accountability frameworks are substantial.
- Companies with strong accountability measures typically experience 15-20% higher investor confidence ratings and demonstrate more resilient performance during market volatility.
Transparency: Illuminating the Path Forward
- Transparency requires companies to provide clear, accurate, and timely information about their activities, policies, and performance to stakeholders.
- This principle has evolved significantly in the digital age, where information accessibility has become paramount.
- A compelling example comes from Patagonia’s radical transparency initiative.
- The outdoor clothing company publishes detailed supply chain information, including factory conditions, environmental impact assessments, and even their failures in sustainability goals.
- This transparency strategy has resulted in:
- Premium brand positioning with 40% higher customer loyalty rates
- Attraction of top talent seeking purpose-driven organizations
- Enhanced investor relations through predictable and honest communications
- Reduced regulatory scrutiny due to proactive disclosure practices
- Recent developments in transparency requirements include the SEC’s new climate disclosure rules, which mandate detailed environmental reporting. Companies implementing comprehensive transparency frameworks are experiencing reduced compliance costs and improved access to ESG-focused investment capital.
Fairness: Equity in Action
- The principle of fairness involves treating all stakeholders—shareholders, employees, customers, and communities—with equity and justice.
- This principle has gained renewed importance as stakeholder capitalism reshapes corporate priorities.
- Salesforce’s pay equity initiative exemplifies fairness in practice.
- The company conducted comprehensive salary audits and invested over $16 million to eliminate pay gaps across gender and ethnicity lines. Their approach included:
- Regular compensation audits with third-party verification
- Transparent promotion criteria accessible to all employees
- Equal representation goals for leadership positions
- Stakeholder feedback mechanisms ensuring diverse perspectives in decision-making
- The economic benefits of fairness-focused governance are measurable.
- Companies with strong fairness practices report 25% lower employee turnover, 30% higher customer satisfaction scores, and improved access to diverse talent pools.
- Responsibility: Ethical Leadership in Practice
- Responsibility emphasizes the duty of directors and executives to act in the best interests of the company and its stakeholders. This principle has expanded to encompass broader societal responsibilities and long-term value creation.
- Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan demonstrates responsibility at scale. The company committed to decoupling business growth from environmental impact while increasing positive social impact. Their responsible governance approach includes:
- Long-term strategic planning with 10-year sustainability targets
- Stakeholder integration in strategic decision-making processes
- Risk management frameworks addressing environmental and social factors
- Performance measurement systems tracking both financial and non-financial metrics
- This responsible approach has generated €1 billion in cost savings through efficiency improvements and positioned Unilever as a preferred partner for environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
Independence: Objective Governance Excellence
- Independence promotes impartiality and objective judgment in corporate decision-making. Independent directors play a crucial role in overseeing management and ensuring decisions align with company and shareholder interests.
- Recent regulatory developments have strengthened independence requirements. The NYSE and NASDAQ have implemented enhanced independence standards, requiring:
- Majority independent board composition for listed companies
- Independent committee leadership for audit, compensation, and nominating committees
- Regular executive sessions without management present
- Comprehensive independence assessments addressing financial and personal relationships
- Companies with highly independent boards demonstrate 12% better long-term stock performance and reduced likelihood of corporate scandals compared to those with less independent governance structures.
- Economic Implications and Future Outlook
The economic impact of strong corporate governance extends beyond individual companies to entire markets. Research indicates that countries with robust governance frameworks experience:
- Higher foreign direct investment flows
- Lower cost of capital for domestic companies
- Increased market liquidity and efficiency
- Enhanced economic stability during crisis periods
Emerging trends in corporate governance include artificial intelligence in board decision-making, enhanced cybersecurity governance, and integrated ESG reporting frameworks. Companies adapting to these developments are positioning themselves for sustained competitive advantage.
Implementation Excellence
- Successful governance implementation requires systematic approaches tailored to organizational contexts.
- Leading companies are adopting technology-enabled governance platforms that provide real-time monitoring, automated compliance tracking, and predictive risk assessment capabilities.
- As businesses continue navigating an increasingly complex global environment, these governance principles serve as essential guideposts for sustainable growth and resilience.
- Organizations that embrace comprehensive governance frameworks are not merely meeting regulatory requirements—they are building foundations for long-term value creation, stakeholder trust, and market leadership in an evolving business landscape.
- The future belongs to companies that view corporate governance not as a compliance burden, but as a strategic advantage that enables sustainable success while contributing positively to society and the global economy.
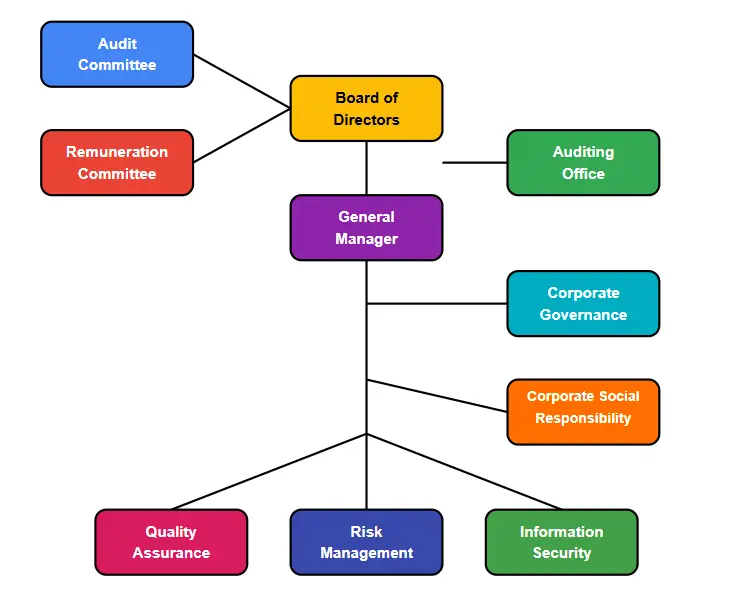
The Critical Role of the Board of Directors in Modern Corporate Governance
- The board of directors stands as the cornerstone of effective corporate governance, serving as the vital bridge between management and stakeholders in today’s complex business environment.
- Far beyond ceremonial oversight, the board’s primary responsibility encompasses strategic direction alignment with shareholder interests while balancing the needs of diverse stakeholders including employees, customers, and communities.
Strategic Oversight and Vision Setting
- The board’s fundamental duty involves establishing and monitoring the organization’s strategic trajectory through several critical mechanisms:
- Vision and Mission Development: Boards actively participate in crafting long-term organizational vision statements that reflect stakeholder values and market realities
- Strategic Plan Approval: Directors rigorously evaluate management’s strategic proposals, ensuring alignment with organizational capabilities and market opportunities
Performance Monitoring: Regular assessment of key performance indicators and strategic milestones to track progress against established objectives - Resource Allocation Oversight: Ensuring optimal distribution of financial and human resources to support strategic initiatives
- Recent developments in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) considerations have fundamentally transformed how boards approach strategic oversight.
- Modern directors must now integrate sustainability metrics, social impact assessments, and governance transparency into their decision-making processes, reflecting evolving stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE CHART: MANAGEMENT FOCUS
Comprehensive Risk Management Framework
- Today’s volatile business environment demands sophisticated risk management approaches that extend far beyond traditional financial risks:
- Enterprise Risk Assessment
- Cybersecurity Threats: Boards now regularly review cybersecurity protocols, data protection measures, and incident response plans
- Regulatory Compliance: Continuous monitoring of evolving regulatory landscapes across multiple jurisdictions
- Reputational Risk Management: Proactive strategies to protect brand integrity and stakeholder trust
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Assessment of global supply chain disruptions and mitigation strategies
Internal Control Systems
- The board ensures robust internal controls through:
- Audit Committee Oversight: Independent review of financial reporting processes and internal audit functions
- Compliance Monitoring: Regular assessment of adherence to legal requirements and industry standards
- Fraud Prevention: Implementation of comprehensive fraud detection and prevention mechanisms Whistleblower Protections: Establishing secure channels for reporting misconduct without retaliation
- Modern risk management increasingly incorporates predictive analytics and scenario planning to anticipate potential challenges before they materialize, enabling proactive rather than reactive governance approaches.
Leadership Excellence and Succession Planning
The board’s responsibility for management oversight has evolved into a comprehensive leadership development function:
Executive Evaluation and Development
- CEO Performance Assessment: Regular, structured evaluation of chief executive performance against predetermined objectives
- Senior Leadership Review: Comprehensive assessment of executive team capabilities and development needs
- Compensation Alignment: Ensuring executive compensation packages align with performance outcomes and stakeholder interests
- ]Leadership Development: Investing in executive coaching, training, and professional development programs
Strategic Succession Planning
- Effective boards maintain robust succession plans that include:
- Emergency Succession Protocols: Immediate leadership transition plans for unexpected circumstances
- Long-term Leadership Pipeline: Development of internal candidates for key positions
- External Candidate Networks: Maintaining relationships with potential external leadership candidates Knowledge Transfer Systems: Ensuring critical institutional knowledge preservation during leadership transitions
Fostering Organizational Culture and Accountability
- The board plays an increasingly vital role in shaping organizational culture through:
- Ethical Leadership Modeling: Demonstrating highest standards of integrity and ethical decision-making
- Transparency Promotion: Encouraging open communication and information sharing throughout the organization
- Diversity and Inclusion: Championing diverse perspectives in leadership and throughout the organization
- Stakeholder Engagement: Facilitating meaningful dialogue with various stakeholder groups
- Cultural transformation initiatives led by engaged boards have proven instrumental in driving organizational performance improvements and stakeholder satisfaction.
The Future of Board Governance
- As business environments continue evolving rapidly, boards must adapt their governance approaches to address emerging challenges including artificial intelligence integration, climate change impacts, and changing workforce dynamics.
- Forward-thinking boards are already implementing digital governance tools, enhancing director education programs, and expanding their oversight capabilities to meet these evolving demands.
- The effectiveness of modern corporate governance ultimately depends on boards that embrace their expanded responsibilities while maintaining focus on their core mission: protecting stakeholder interests while enabling sustainable organizational success.
- Through comprehensive oversight, proactive risk management, and strategic leadership development, boards continue serving as the foundation of corporate accountability and long-term value creation.
A Comprehensive Framework for Modern Business Leadership
- As we advance into 2028, the corporate governance landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, driven by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and heightened stakeholder expectations.
- Companies that fail to adapt their governance frameworks risk not only regulatory penalties but also competitive disadvantage in an increasingly transparent marketplace.
- The convergence of environmental pressures, social responsibility demands, and technological disruption has created a perfect storm that requires sophisticated governance responses.
ESG Integration and Accountability: Beyond Compliance to Strategic Advantage
- The integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria has transcended mere compliance requirements to become a fundamental driver of business strategy and value creation.
- Companies are discovering that robust ESG frameworks not only satisfy regulatory demands but also unlock new opportunities for innovation, cost reduction, and market differentiation.
Strategic ESG Implementation Framework:
- Materiality Assessment and Goal Setting: Companies must conduct comprehensive materiality assessments to identify ESG factors that significantly impact their business operations and stakeholder value.
- This involves engaging with investors, customers, employees, and communities to understand their priorities and expectations.
- Integrated Reporting Systems: Modern governance requires sophisticated reporting mechanisms that seamlessly integrate ESG metrics with financial performance indicators. Companies are implementing real-time dashboards that provide board members and executives with continuous visibility into ESG performance.
- Stakeholder Engagement Platforms: Leading organizations are establishing formal stakeholder engagement programs that go beyond traditional shareholder communications.
- These platforms facilitate regular dialogue with diverse stakeholder groups, ensuring that governance decisions reflect broader community interests.
- Performance Measurement and Accountability: Companies are developing quantitative ESG metrics that directly link to executive compensation and board evaluation criteria. This includes carbon reduction targets, diversity metrics, and social impact measurements that are regularly audited and publicly reported.
- Supply Chain ESG Integration: Forward-thinking companies are extending ESG requirements throughout their supply chains, implementing vendor assessment programs and requiring ESG compliance from key partners and suppliers.
- The financial implications of ESG integration are becoming increasingly clear, with studies showing that companies with strong ESG performance often demonstrate superior long-term financial returns and reduced risk profiles.
- This has led to the emergence of ESG-linked financing instruments and investment products that reward companies for measurable ESG improvements.
Board Diversity and Inclusion Excellence: Building High-Performance Governance Teams
- Board diversity has revolved from a regulatory checkbox to a strategic imperative that directly impacts organizational performance and innovation capacity.
- Research consistently demonstrates that diverse boards make better decisions, provide more effective oversight, and drive superior financial performance.
- Comprehensive Diversity Strategy Components:
- Multi-Dimensional Diversity Framework: Modern board composition strategies address diversity across multiple dimensions including gender, ethnicity, age, professional background, industry experience, and cognitive diversity.
- Companies are moving beyond simple demographic targets to focus on creating boards with complementary skill sets and perspectives.
- Succession Planning and Pipeline Development: Leading organizations are implementing robust succession planning processes that identify and develop diverse candidates years in advance.
- This includes partnerships with professional organizations, executive search firms, and leadership development programs focused on underrepresented groups.
- Inclusive Board Culture Development: Creating diverse boards is only the first step; companies must also foster inclusive cultures where all board members feel empowered to contribute their unique perspectives.
- This involves structured onboarding programs, mentorship initiatives, and regular culture assessments.
- Skills-Based Recruitment: Companies are adopting competency-based board recruitment processes that prioritize specific skills and experiences needed for strategic oversight.
- This includes digital expertise, cybersecurity knowledge, sustainability experience, and international market understanding.
- Performance Evaluation and Development: Regular board evaluations now include assessments of diversity and inclusion effectiveness, with specific metrics for measuring the contribution of diverse perspectives to board decision-making processes.
- The business case for board diversity continues to strengthen, with companies reporting improved risk management, enhanced strategic planning, and better stakeholder relationships as direct results of more diverse governance structures.
Digital Transformation and Cybersecurity Governance: Navigating the Digital Risk Landscape
- Digital transformation has fundamentally altered the risk and opportunity landscape for modern corporations, requiring boards to develop new competencies and oversight mechanisms.
- The rapid acceleration of digital adoption, particularly following global disruptions, has made digital governance a critical success factor.
- Digital Governance Excellence Framework:
- Digital Literacy and Board Education: Boards must invest in continuous education programs to develop digital fluency among directors. This includes regular briefings on emerging technologies, cybersecurity threats, and digital market trends that could impact business strategy.
- Cybersecurity Risk Management: Companies are implementing comprehensive cybersecurity governance frameworks that include regular threat assessments, incident response planning, and board-level cybersecurity committees with specialized expertise.
- Data Governance and Privacy Compliance: With increasing data privacy regulations worldwide, boards must oversee robust data governance programs that ensure compliance while enabling data-driven business strategies. This includes privacy impact assessments, data retention policies, and third-party data sharing agreements.
- Technology Investment Oversight: Boards are developing sophisticated processes for evaluating and overseeing major technology investments, including artificial intelligence implementations, cloud migration strategies, and digital platform developments.
- Digital Ethics and AI Governance: As artificial intelligence becomes more prevalent in business operations, boards must establish ethical frameworks for AI deployment, including bias prevention, algorithmic transparency, and responsible automation strategies.
- The integration of digital governance requires boards to balance innovation opportunities with risk management, ensuring that companies can capitalize on technological advances while maintaining appropriate controls and safeguards.
Emerging Governance Trends for 2025: Anticipating Future Challenges
- The governance landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with several emerging trends that forward-thinking companies are already beginning to address.
- These developments represent both opportunities and challenges that will shape corporate governance practices in the coming years.
- Key Emerging Governance Areas:
- Climate Risk Integration: Companies are implementing comprehensive climate risk assessment and management frameworks that address both physical and transition risks associated with climate change. This includes scenario planning, stress testing, and integration of climate considerations into strategic planning processes.
- Stakeholder Capitalism Implementation: The shift toward stakeholder capitalism requires new governance mechanisms that balance the interests of shareholders, employees, customers, communities, and the environment.
- Companies are developing stakeholder impact measurement systems and governance structures that ensure all stakeholder voices are heard.
- Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Adoption: Advanced companies are leveraging technology solutions to enhance compliance monitoring, regulatory reporting, and risk management processes.This includes automated compliance systems, real-time monitoring platforms, and predictive analytics for regulatory risk assessment.
- Human Capital Management: Boards are taking iincreased responsibility for human capital oversight, including workforce development, employee engagement, and talent retention strategies. This reflects growing recognition that human capital is often a company’s most valuable asset.
- Geopolitical Risk Management: In an increasingly complex global environment, boards must develop sophisticated approaches to managing geopolitical risks, including trade tensions, regulatory changes, and supply chain disruptions.
Implementation Roadmap: Translating Best Practices into Action
- Successfully implementing these governance best practices requires a structured approach that considers organizational readiness, resource requirements, and change management needs.
- Phased Implementation Strategy:
- Assessment and Gap Analysis: Conduct comprehensive assessments of current governance practices against best practice standards, identifying priority areas for improvement and resource requirements.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Buy-In: Secure commitment from key stakeholders, including board members, senior executives, and major shareholders, for governance transformation initiatives.
- Pilot Program Development: Implement governance improvements through carefully designed pilot programs that allow for testing, refinement, and learning before full-scale deployment.
- Technology and Infrastructure Investment: Invest in the technology platforms, data systems, and analytical capabilities needed to support modern governance practices.
- Training and Development Programs: Implement comprehensive training programs for board members, executives, and staff to develop the competencies needed for effective governance in the modern business environment.
- • Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Establish ongoing monitoring and evaluation processes that ensure governance practices continue to evolve and improve over time.
- The companies that successfully navigate the governance challenges of 2025 will be those that view governance not as a compliance burden but as a strategic capability that drives competitive advantage, stakeholder value, and long-term sustainability.
- By embracing these best practices and maintaining a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can build governance frameworks that support success in an increasingly complex and dynamic business environment.
- As we move forward into 20288, the most successful companies will be those that recognize corporate governance as a dynamic, evolving discipline that requires continuous attention, investment, and innovation.
- The governance frameworks that emerge from this period of transformation will likely define business success for years to come.
A Comprehensive Guide to Current Challenges and Opportunities
- Securities litigation represents one of the most complex and rapidly evolving areas of corporate law, encompassing legal disputes that arise from violations of federal and state securities regulations.
- These cases fundamentally protect market integrity by addressing fraud, misrepresentation, and other misconduct in the buying, selling, or holding of securities.
Understanding the Core Components
- Securities litigation encompasses several critical areas that investors and corporations must navigate:
- Fraud on the Market Theory: This foundational principle allows investors to rely on market efficiency, presuming that material misrepresentations affect stock prices and harm all investors who traded during the fraud period
- Insider Trading Violations: Cases involving the illegal use of material, non-public information to gain unfair trading advantages
- Market Manipulation: Schemes designed to artificially inflate or deflate security prices through deceptive practices
- Accounting Fraud: Misstatements in financial reports that mislead investors about a company’s true financial condition
- Breach of Fiduciary Duty: Violations where corporate officers or directors fail to act in shareholders’ best interests
Recent Developments Reshaping the Landscape
- The securities litigation environment has experienced significant changes in 2024, fundamentally altering how cases are prosecuted and defended:
- Supreme Court Impact: The unanimous decision in Macquarie Infrastructure Corp. v. Moab Partners, L.P. has reshaped pleading standards for omissions in private securities fraud actions.
- This landmark ruling clarifies when companies have a duty to disclose information, raising the bar for plaintiffs while providing clearer guidance for corporate disclosure obligations.
- Artificial Intelligence Disclosure Requirements: As AI integration accelerates across industries, companies face mounting pressure to disclose AI-related risks and implementations.
- The regulatory patchwork of federal and state-level AI initiatives creates new compliance challenges, with securities litigation increasingly targeting inadequate AI disclosures.
- Statistical Trends: In 2024, federal courts saw 229 new securities class action lawsuits filed, maintaining consistent levels with previous years.
- Technology and healthcare sectors continue to dominate filings, reflecting ongoing scrutiny of rapidly evolving industries where disclosure challenges are most pronounced.
The Fraud on the Market Theory: Current Applications
- Recent developments have refined how courts apply the fraud on the market theory, particularly regarding:
- Market Efficiency Requirements: Courts now scrutinize more carefully whether markets are truly efficient enough to support the presumption of reliance
- Price Impact Analysis: Enhanced economic analysis is required to demonstrate that alleged misrepresentations actually affected stock prices
- Rebuttal Strategies: Defendants increasingly challenge the theory by presenting evidence that specific information did not impact market prices
- Class Certification Challenges: The theory’s application in class certification has become more rigorous, requiring stronger economic evidence
Practical Risk Management Strategies
- For Corporations: Companies must implement comprehensive compliance frameworks that address evolving litigation risks:
- Enhanced Disclosure Protocols: Develop robust systems for identifying and disclosing material information, particularly regarding emerging technologies and regulatory changes
- AI Governance Programs: Establish clear policies for AI implementation, risk assessment, and disclosure requirements
- Regular Legal Audits: Conduct periodic reviews of disclosure practices and potential litigation exposures
- Executive Training: Ensure leadership understands their disclosure obligations and potential personal liability
- For Investors: Understanding securities litigation empowers investors to protect their rights and seek appropriate remedies:
- Document Preservation: Maintain detailed records of investment decisions and communications
- Stay Informed: Monitor corporate disclosures and regulatory developments that may affect investments
- Timely Action: Understand statute of limitations requirements for bringing securities litigation claims
- Professional Guidance: Consult with experienced securities litigation attorneys when potential violations are identified
The Path Forward
- Securities litigation continues evolving as markets become more complex and regulatory frameworks adapt to technological advancement.
- The intersection of traditional securities law with emerging technologies creates new challenges requiring sophisticated legal and economic analysis.
- Companies that prioritize transparency and implement comprehensive risk management programs position themselves to navigate this complex landscape successfully.
- Proactive compliance measures not only reduce litigation risk but also enhance investor confidence and market reputation.
- For investors, understanding these legal mechanisms provides essential protection in an increasingly complex financial environment.
- Securities litigation serves as a crucial deterrent against corporate misconduct while providing pathways for recovery when violations occur.
- The regulatory environment will continue evolving, making it essential for all market participants to stay informed about legal developments and maintain robust compliance programs.
- By understanding both the challenges and opportunities within securities litigation, companies and investors can better protect their interests while contributing to overall market integrity.
Conclusion: The Future of Corporate Governance and Securities Litigation
As we look to the future, the landscape of corporate governance and securities litigation will continue to evolve, driven by emerging trends, technological advancements, and changing stakeholder expectations.
Companies must remain vigilant and proactive in adapting to these changes, ensuring that their governance frameworks are robust, transparent, and aligned with their strategic objectives.
By embracing best practices in corporate governance and risk management, companies can enhance their ability to navigate the complex and dynamic business environment, ultimately driving long-term value creation and sustainability.
The integration of ESG considerations into corporate governance will be a key focus for companies in the coming years, as investors and regulators demand greater accountability and transparency in environmental, social, and governance matters.
Companies that successfully integrate ESG into their governance frameworks will be better positioned to address sustainability challenges, enhance stakeholder trust, and capitalize on new opportunities.
Additionally, the growing importance of diversity and inclusion will continue to shape corporate governance, with companies striving to build more diverse and inclusive boards that reflect the communities they serve.
In the realm of securities litigation, companies must remain vigilant in understanding and managing the legal and regulatory risks associated with their business activities.
This includes staying informed about changes in securities laws and regulations, implementing robust compliance and risk management programs, and leveraging technology to enhance their governance and risk management capabilities.
By taking proactive measures to address securities litigation risks, companies can protect their interests, maintain investor confidence, and ensure their long-term success in an increasingly complex and competitive marketplace.
Contact Timothy L. Miles Today for a Free Case Evaluation
If you suffered substantial losses and wish to serve as lead plaintiff in a securities class action, or have questions about securities class action settlements, or just general questions about your rights as a shareholder, please contact attorney Timothy L. Miles of the Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles, at no cost, by calling 855/846-6529 or via e-mail at [email protected]. (24/7/365).
Timothy L. Miles, Esq.
Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles
Tapestry at Brentwood Town Center
300 Centerview Dr. #247
Mailbox #1091
Brentwood,TN 37027
Phone: (855) Tim-MLaw (855-846-6529)
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.classactionlawyertn.com
Facebook Linkedin Pinterest youtube
Visit Our Extensive Investor Hub: Learning for Informed Investors