Understanding Fraud in the Financial Sector: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Different types of fraud presents many triggers to securities ligation as well as enforcement actions from regulatory bodies
- Fraud in the financial sector is not just a modern-day phenomenon; it is a persistent issue that has plagued markets for decades.
- As financial systems have evolved, so too have the methods by which unscrupulous actors attempt to manipulate them.
- At its core, accouting fraud involves deceit, trickery, or a breach of confidence, all executed with the intent to gain an unfair or unlawful advantage.
- From individuals peddling fake investment schemes to corporations manipulating their financial statements, the range of fraudulent activities is vast, and the impact can be devastating for both individual and institutional investors.
The Evolution of Financial Deception and the Different Types of Fraud
- Historical patterns reveal that financial fraud has adapted remarkably to each era’s dominant technologies and market structures.
- The railroad speculation bubbles of the 1800s gave way to securities manipulation in the early 1900s, which evolved into sophisticated aaccounting fraud by the late 20th century.
- Today’s fraudsters exploit artificial intelligence, cryptocurrency platforms, and social media to reach unprecedented numbers of potential victims with minimal effort.
- Recent developments demonstrate this evolution clearly. Deepfake technology now enables fraudsters to create convincing video testimonials from fake executives, while algorithmic trading manipulation allows for microsecond-level market abuse that traditional oversight mechanisms struggle to detect.
- The 2023 emergence of AI-generated financial reports has created entirely new categories of potential securities violations.
Modern Fraud Mechanisms and Market Impact
The repercussions of financial fraud extend far beyond the immediate financial losses suffered by victims. Fraud undermines trust in the financial system, which is a fundamental pillar of market operations. When investors lose confidence in the equity of markets, the ripple effects can lead to increased volatility, reduced investment, and a slowing of economaccouting fraudic growth. Market confidence erosion following major fraud revelations typically results in:
- Immediate liquidity contractions as institutional investors withdraw from affected sectors
- Regulatory overcorrection that can stifle legitimate innovation
- Increased compliance costs that disproportionately burden smaller market participants
- Long-term reputational damage to entire industry segments
The 2024 cryptocurrency exchange collapses illustrate these cascading effects perfectly. When several major platforms were revealed to have engaged in customer fund misappropriation, the entire digital asset sector experienced a 40% market capitalization decline within weeks, affecting even legitimate operators.
Technological Amplification of Risk
- Technological advancements have added layers of complexity to accouting fraud.
- While technology has enabled faster and more efficient transactions, it has also provided fraudsters with new tools and methods to perpetrate their schemes.
- Cybersecurity threats, such as phishing and hacking, have become more prevalent, making it imperative for financial institutions and investors to be proactive in their defense strategies.
- Machine learning algorithms now enable fraudsters to analyze vast datasets of investor behavior, allowing them to craft highly personalized scams that exploit individual psychological vulnerabilities.
- Social engineering attacks have become so sophisticated that they can mimic trusted financial advisors’ communication patterns with startling accuracy.
- The digital age demands that everyone involved in the financial sector stay informed about potential risks and remain vigilant against ever-evolving fraudulent tactics.
- Real-time accouting fraud detection systems employing behavioral analytics have become essential, yet they create new privacy concerns and potential discrimination issues that regulators are still addressing.
Recent Regulatory Developments
- Regulatory responses to emerging fraud patterns have intensified significantly.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission’s 2024 enforcement actions resulted in $8.2 billion in penalties, representing a 35% increase from the previous year.
- New regulations specifically targeting AI-generated content in financial communications require clear disclosure when artificial intelligence contributes to investment recommendations or market analysis.
- International coordination has also strengthened, with cross-border accouting fraud investigations now sharing real-time intelligence through automated systems.
- The Financial Action Task Force’s updated guidelines mandate that financial institutions implement enhanced due diligence protocols for transactions involving emerging technologies.

Protecting Market Integrity
- By understanding the landscape of accouting fraud, stakeholders can better navigate the challenges and safeguard their financial interests.
- Proactive defense strategies must now encompass both traditional due diligence and cutting-edge technological awareness.
- Investors should verify the authenticity of digital communications through multiple channels and remain skeptical of investment opportunities that promise unusually high returns with minimal risk.
- Financial institutions bear increasing responsibility for implementing robust fraud prevention systems while maintaining the efficiency that modern markets demand.
- This balance requires continuous investment in both technology and human expertise, creating ongoing challenges for resource allocation and strategic planning.
- The future of accouting fraud prevention lies in collaborative intelligence sharing between institutions, regulators, and technology providers, ensuring that defensive capabilities evolve as rapidly as the threats they aim to counter.
Securities Class Actions and Fraud: A Comprehensive Analysis of Investor Protection Mechanisms
The Evolution and Impact of Securities Class Actions
- Securities class actions have fundamentally transformed how investors seek redress for financial market misconduct, emerging as the primary legal mechanism for addressing widespread securities fraud.
- Securities litigation enable investors who suffered similar harm from fraudulent activities to consolidate their claims, creating a powerful deterrent against corporate malfeasance while ensuring efficient judicial resource utilization.
- The financial impact of these actions cannot be overstated. In 2024, securities class action settlements totaled over $4.75 billion.
- This represents a significant increase from previous years, reflecting both the growing sophistication of accouting fraud schemes and the enhanced effectiveness of legal remedies.
- The deterrent effect extends beyond immediate financial penalties, as companies now invest substantially more in compliance programs and internal controls to avoid potential litigation exposure.
- The Supreme Court’s 2024 decision in Macquarie Infrastructure Corp. v. Moab Partners, L.P., 601 U.S. 257 (2024) (vacated and remanded, April 12, 2005) (no pet. for r’hearng filed) fundamentally reshaped pleading standards for omission claims, requiring plaintiffs to demonstrate more clearly that defendants had a duty to disclose the omitted information.
- This development has made it crucial for investors to understand the evolving legal landscape when considering participation in securities litigation.
- The procedural advantages of class actions include cost-sharing among plaintiffs, access to top-tier legal representation, and the ability to pursue claims that might be economically unfeasible individually.
- However, investors must also understand the 90-day look-back provision under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act (PSLRA), which can limit damage calculations for investors who hold securities for extended periods after corrective disclosures.
Sophisticated Fraud Schemes: Beyond Traditional Models
Ponzi Schemes in the Digital Age
- Modern Ponzi schemes have evolved significantly from Charles Ponzi’s original mail coupon arbitrage scheme. Contemporary variations often involve cryptocurrency platforms, online investment portals, and sophisticated marketing through social media influencers.
- The 2022 collapse of the FTX cryptocurrency exchange exemplifies how traditional Ponzi elements can manifest in cutting-edge financial technologies, resulting in $8 billion in investor losses.
- Detection mechanisms have also advanced, with regulatory bodies insider tradnow employing artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious trading patterns and cash flow irregularities that characterize Ponzi operations.
- The SEC’s enhanced analytical capabilities have led to earlier intervention in many cases, though the global and digital nature of modern schemes presents ongoing challenges.
Insider Trading: Evolving Enforcement and New Frontiers
- For 2024, the SEC collected $8.2 billion in financial remedies consisted of $6.1 billion in disgorgement and prejudgment interest, also the highest amount on record, and $2.1 billion in civil penalties, the second-highest amount on record.
- Sophisticated detection methods now include analysis of trading patterns, communication metadata, and even social media activity to identify potential violations.
- The rise of algorithmic trading has created new categories of insider trading violations, where material non-public information can be exploited within milliseconds of acquisition.
- Recent enforcement actions have targeted novel forms of insider trading, including the misuse of alternative data sources such as satellite imagery, credit card transaction data, and social media sentiment analysis.
- These cases demonstrate how the definition of material non-public information continues to expand in our data-driven economy.

Accounting Fraud: Modern Manifestations and the Response by Regulatory Bodies
- Contemporary aaccounting fraud has become increasingly sophisticated, often involving complex financial instruments, off-balance-sheet entities, and revenue recognition manipulation.
- The implementation of new accounting standards like ASC 606 (Revenue Recognition) has created both opportunities for legitimate earnings management and potential avenues for fraudulent activity.
- Technology-enabled accounting fraud detection has revolutionized how accounting irregularities are identified.
- Advanced analytics can now detect unusual journal entries, identify patterns consistent with earnings manipulation, and flag transactions that deviate from historical norms.
- The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board’s (PCAOB) enhanced audit requirements have also strengthened the external verification processes that help prevent and detect accounting fraud.
Recent Developments in Fraud Prevention and Market Integrity
- The integration of artificial intelligence in both fraud perpetration and detection represents a significant recent development.
- While AI enables more sophisticated fraud schemes, it also provide regulators and market participants with powerful tools for real-time monitoring and pattern recognition.
- The SEC’s new AI disclosure requirements mandate that companies provide detailed information about their AI usage, creating both transparency and potential liability exposure.
- Whistleblower programs have proven increasingly effective, with the SEC awarding over $255 million to 47 whistleblowers in Fiscal Year 2024.
- These programs have evolved to provide stronger protections and clearer reporting mechanisms, encouraging insiders to report accounting fraud before they cause widespread investor harm.
- The global coordination of securities enforcement has also strengthened significantly. International cooperation agreements now enable rapid information sharing and coordinated enforcement actions across jurisdictions, making it more difficult for fraudsters to exploit regulatory arbitrage opportunities.
- Market structure changes, including the growth of special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs) and direct listings, have created new areas of focus for regulatory bodies.
- The SEC has implemented enhanced disclosure requirements and heightened scrutiny of SPAC transactions, responding to concerns about potential investor protection gaps in these alternative public offering mechanisms.
- For investors navigating this complex landscape, understanding these evolving accounting fraud patterns and responses to regulatory bodies is essential for making informed investment decisions and recognizing potential red flags.
- The continued strengthening of legal remedies through securities class actions provides crucial protection, but investor education and vigilance remain the first line of defense against fraudulent schemes.
The Evolving Landscape of Securities Fraud in Class Action Litigation
- Securities litigation continues to serve as the cornerstone of class action litigation, creating a vital mechanism for investor protection in increasingly complex financial markets.
- These fraudulent activities—encompassing misleading statements, material omissions, and manipulative trading practices—fundamentally distort market pricing mechanisms and compromise the integrity of investment decisions.
- When corporations engage in deceptive practices, they create artificial inflation in securities prices, leading investors to make decisions based on fundamentally flawed information.
Recent Developments in Accouting Fraud on the Market Theory
- The fraud on the market theory has undergone significant evolution in recent years, particularly following landmark Supreme Court decisions that have reshaped how courts analyze market efficiency and investor reliance.
- This theory, which presumes that investors rely on market prices that reflect all publicly available information, has become increasingly sophisticated in its application.
- Recent judicial developments have emphasized the importance of market efficiency analysis in establishing fraud on the market presumptions.
- Courts now require more rigorous examination of whether securities trade in efficient markets, considering factors such as trading volume, analyst coverage, and the speed with which new information is incorporated into stock prices.
- This heightened scrutiny has led to more nuanced approaches to class certification, where defendants increasingly challenge the efficiency of markets for their securities.
- The Basic, Inc. v. Levinson, 485 U.S. 224 (1988) framework continues to evolve, with recent circuit court decisions providing clearer guidance on how to evaluate market efficiency in today’s algorithmic trading environment.
- These developments have particular significance for technology companies and smaller-cap securities, where traditional markers of market efficiency may not apply as clearly.
Enhanced Materiality Standards and Their Application in Securities Litigation
- The materiality requirement has become increasingly sophisticated, moving beyond the traditional “total mix” standard to incorporate more nuanced analyses of information significance.
- Material misrepresentations must now be evaluated not just for their potential impact on reasonable investors, but also for their actual market impact as demonstrated through empirical analysis.
- Recent cases have established that materiality determinations must consider the temporal context of disclosures, the competitive landscape in which companies operate, and the sophistication level of the investor base.
- This evolution reflects courts’ recognition that different types of information carry varying weight depending on industry dynamics and market conditions.
- Expert testimony has become crucial in establishing materiality, with forensic accountants and market efficiency experts providing detailed analyses of how specific misrepresentations affected trading patterns and investor decision-making processes.
- These expert analyses often incorporate advanced statistical methods to demonstrate the causal relationship between fraudulent disclosures and market reactions.

Market Impact Analysis and Investor Protection Mechanisms
- The impact of securities fraud extends far beyond individual investor losses, creating systemic risks that can undermine market confidence and efficiency.
- Event studies have become essential tools for quantifying these impacts, providing empirical evidence of how fraudulent activities distort natural price discovery mechanisms.
- Modern securities class actions increasingly rely on sophisticated economic modeling to demonstrate both the existence of artificial inflation and its subsequent removal from securities prices.
- These models consider multiple variables, including industry trends, broader market movements, and company-specific factors that might influence stock price movements independent of the alleged accounting fraud.
- The loss causation analysis in securities litigation has become particularly complex, requiring plaintiffs to demonstrate not only that fraud occurred, but that the subsequent price decline resulted specifically from the revelation of that fraud rather than other market forces.
This requirement has led to more detailed pleading standards and more rigorous expert analysis in securities litigation.
Strengthening Market Integrity Through Legal Remedies
- Securities class actions serve as a critical deterrent mechanism against corporate misconduct, creating financial consequences that encourage companies to maintain accurate disclosure practices.
- The threat of substantial damages awards motivates corporations to invest in robust compliance systems and internal controls designed to prevent fraudulent activities.
- Institutional investors have increasingly taken leadership roles in securities class actions, bringing sophisticated resources and experience to litigation that benefits all class members.
- These institutional lead plaintiffs often have the financial capacity to pursue complex litigation against well-funded defendants, leveling the playing field in securities disputes.
- The settlement process in securities class actions has evolved to provide more efficient resolution of claims while ensuring adequate compensation for harmed investors.
- Recent settlements have incorporated innovative distribution mechanisms that better account for different types of investor harm and trading patterns.
Practical Implications for Modern Investors
- Understanding these evolving legal standards empowers investors to better protect their interests and seek appropriate remedies when fraud occurs.
- Due diligence practices should now incorporate awareness of these legal developments, helping investors recognize potential red flags and understand their rights when fraudulent activities are suspected.
- The increasing sophistication of securities litigation means that investors benefit from legal representation that understands both traditional securities law principles and emerging trends in market analysis.
- Early intervention in potential securities class actions can be crucial for preserving evidence and establishing strong legal positions.
- Securities class actions continue to evolve as essential tools for maintaining market integrity, providing both individual remedies and systemic deterrence against fraudulent activities.
- As markets become increasingly complex and interconnected, these legal mechanisms serve as vital safeguards for investor confidence and market efficiency.
How to Identify Fraudulent Activities
- Detecting fraudulent activities in the financial sector requires vigilance and a keen understanding of the warning signs that often accompany such misconduct.
- One of the most effective ways to identify potential fraud is by closely analyzing financial statements and disclosures from companies.
- Look for red flags such as inconsistencies in reported earnings, unusually high returns that seem too good to be true, and a lack of transparency in the company’s operations or financial reporting.
- Discrepancies in financial documents can often indicate manipulation or misrepresentation, suggesting a deeper problem that warrants further investigation.
- Investors should also be wary of aggressive sales tactics and pressure to invest quickly without conducting due diligence.
- Fraudsters often employ high-pressure tactics to rush investors into making decisions without thoroughly evaluating the risks involved.
- If an investment opportunity seems urgent or the returns promised are exceptionally high without a clear explanation of the underlying strategy, it is essential to proceed with caution.
- Conducting independent research and seeking advice from financial professionals can provide valuable insights and help differentiate legitimate opportunities from potential scams.
- Staying informed about market trends and updates from regulatory bodies is another critical aspect of identifying fraudulent activities.
- Regulatory bodies frequently issue alerts and guidelines regarding emerging fraud schemes and potential risks. By staying updated on these developments, investors can better protect themselves against evolving threats.
- Additionally, participating in investor education programs and forums can enhance awareness of common fraud tactics and empower investors to make informed decisions.
- Knowledge and vigilance are the best defenses against falling victim to financial fraud, enabling investors to safeguard their assets and contribute to a transparent and fair marketplace.

Legal Framework Governing Securities Class Actions: A Comprehensive Analysis
- The legal framework governing securities class actions built upon a robust foundation of federal and state laws designed to protect investors and maintain the integrity of financial markets.
- This comprehensive regulatory structure has undergone significant refinement over the decades, with recent developments fundamentally reshaping how courts approach securities fraud claims.
Foundational Federal Securities Laws
- The Securities Act of 1933 serves as the cornerstone of investor protection, establishing the principle that transparency must govern all public securities offerings.
- This landmark legislation requires comprehensive registration of securities with the SEC and mandates that issuers provide full and fair disclosure of all material information.
- The Act’s anti-fraud provisions create a strict liability framework for material misstatements in registration statements, providing investors with powerful remedies when companies fail to meet disclosure obligations.
- Building upon this foundation, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 established the SEC as the primary federal regulator and granted it broad authority to oversee secondary market trading.
- This Act addresses critical issues including insider trading, market manipulation, and ongoing reporting requirements for publicly traded companies.
- Most significantly for class action litigation, the Exchange Act provides the statutory basis for Rule 10b-5, which has become the primary vehicle for private securities fraud litigation.
- Rule 10b-5 prohibits fraudulent activities “in connection with the purchase or sale of any security,” creating a broad anti-fraud provision that encompasses material misrepresentations, omissions of material facts, and manipulative trading practices.
- This rule serves as the cornerstone for the majority of securities class actions, allowing investors to seek redress when companies make false or misleading statements that artificially inflate stock prices.
The Fraud on the Market Theory: Recent Developments and Applications
- The Fraud on the Market Theory has undergone significant evolution in recent years, fundamentally altering how courts approach securities class action litigation.
- This theory, first recognized by the Supreme Court in Basic Inc. v. Levinson (1988), establishes a rebuttable presumption that investors rely on the integrity of market prices when making investment decisions in efficient markets.
- Recent judicial developments have refined the application of this theory in several crucial ways. Courts now require more rigorous analysis of market efficiency, examining factors such as trading volume, analyst coverage, and the speed with which new information is incorporated into stock prices.
- The theory’s application has become particularly complex in cases involving algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading, where traditional notions of market efficiency must be reconsidered in light of technological advances.
- Contemporary courts have also grappled with the theory’s application to emerging markets and cryptocurrency transactions.
- Recent decisions have established that the fraud on the market presumption may not apply to thinly traded securities or markets lacking sufficient analyst coverage and institutional participation.
- This evolution reflects the courts’ recognition that market efficiency exists on a spectrum rather than as a binary characteristic.
- The materiality standard under the fraud on the market theory has also seen significant refinement. Courts now apply a more nuanced analysis of whether alleged misrepresentations would significantly alter the “total mix” of information available to investors.
- This includes consideration of how sophisticated institutional investors, who increasingly dominate trading volumes, process and react to corporate disclosures.
Enhanced Federal-State Legal Integration
- The interplay between federal securities laws and state “Blue Sky Laws” has become increasingly sophisticated, creating a multi-layered regulatory framework that provides comprehensive investor protection.
- State securities laws vary significantly in their approach, with some states adopting merit review standards that go beyond federal disclosure requirements to evaluate the fairness of securities offerings.
- Concurrent jurisdiction issues have become particularly complex in cases involving both federal securities violations and state law claims.
- Recent court decisions have clarified that state law claims alleging securities fraud must meet heightened pleading standards similar to those required under federal law, particularly regarding scienter and loss causation requirements.
- ]The Securities Litigation Uniform Standards Act (SLUSA) has created additional complexity by preempting certain state law securities class actions while preserving others.
- Courts continue to refine the boundaries of SLUSA preemption, particularly in cases involving derivative instruments and investment contracts that may not fall squarely within traditional securities definitions.
Contemporary Challenges and Evolving Standards
- Modern securities litigation faces unprecedented challenges related to artificial intelligence disclosures, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) claims, and cybersecurity incident reporting.
- Companies increasingly face securities fraud allegations related to inadequate disclosure of AI implementation risks, climate change impacts, and data breach consequences.
- Algorithmic trading has fundamentally altered market dynamics, requiring courts to reconsider traditional assumptions about market efficiency and investor behavior.
- The rise of retail trading platforms and social media-driven investment decisions has created new categories of potential securities violations, particularly regarding market manipulation through coordinated online campaigns.
- Cryptocurrency and digital asset litigation represents an entirely new frontier for securities class actions.
- Courts are still developing frameworks for determining when digital assets constitute securities and how traditional fraud on the market principles apply to decentralized trading platforms and blockchain-based transactions.
Practical Implications for Modern Securities Litigation
- The evolving legal framework creates both opportunities and challenges for investors seeking redress through securities class actions.
- Enhanced pleading standards require more sophisticated factual development at the complaint stage, often necessitating extensive pre-filing investigation and expert analysis.
- Damage calculation methodologies have become increasingly complex, incorporating advanced econometric models to isolate the impact of alleged fraud from other market factors.
- Courts now require more rigorous analysis of loss causation, demanding clear evidence that stock price declines resulted from disclosure of the alleged fraud rather than general market conditions or company-specific factors unrelated to the misconduct.
- Class certification standards continue to evolve, with courts applying more stringent analysis of whether common issues predominate over individual questions.
- This is particularly challenging in cases involving mixed motives for investment decisions or sophisticated institutional investors who may have conducted independent due diligence.
The Process of Filing a Securities Class Action
- Filing a securities class action is a meticulous process that involves several key stages, each requiring careful planning and execution.
- The first step is the filing of a complaint, which outlines the allegations of fraud and the legal basis for the claims.
- This document must detail the specific misrepresentations or omissions that occurred, the material impact on the security’s price, and the intent or negligence of the defendants.
- The complaint serves as the foundation for the lawsuit, setting the stage for the subsequent legal proceedings.
- Once the complaint is filed, the next critical stage is the certification of the class.
- The court must determine whether the case is suitable to proceed as a class action, which involves assessing factors such as the commonality of legal or factual questions among the class members, the adequacy of the class representatives, and the predominance of common issues over individual ones.
- Class certification is a pivotal moment in the litigation process, as it validates the collective nature of the lawsuit and enables the plaintiffs to pursue their claims as a unified group.
- Following class certification, the discovery phase commences, during which both parties gather and exchange evidence relevant to the case.
- This phase can be extensive, involving the review of documents, depositions of witnesses, and expert testimony.
- The discovery process is crucial for building a strong case, as it uncovers the evidence needed to support the allegations of fraud. Once discovery is complete, the parties may proceed to trial or seek a settlement agreement
- Throughout the process, skilled legal representation is essential to navigate the complexities of securities litigation and achieve a favorable outcome for the class.
SECURITIES CLASS ACTION LAWSUITS PROCESS
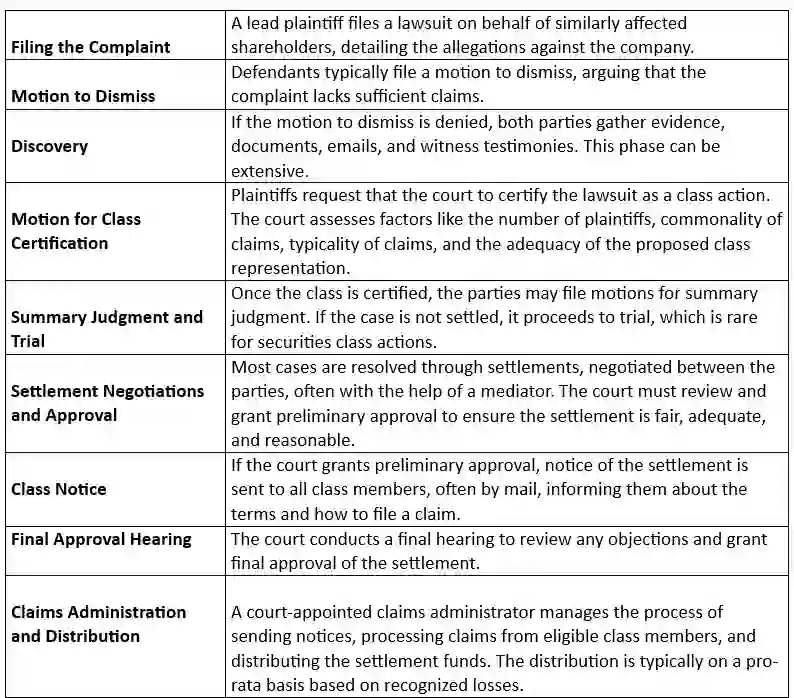
Preventative Measures Against Fraud
- Preventing financial fraud requires a proactive approach that involves both individual vigilance and systemic safeguards.
- One of the most effective preventative measures is the implementation of robust internal controls within organizations.
- These controls include policies and procedures designed to ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial reporting, as well as the detection and prevention of fraudulent activities.
- Regular audits and compliance checks are essential components of a strong internal control system, providing assurance that financial operations are conducted transparently and ethically.
- Investors can also take steps to protect themselves from fraud by conducting thorough due diligence before making investment decisions.
- This involves researching potential investment opportunities, verifying the credentials of financial advisors, and scrutinizing the financial statements and disclosures of companies.
- Being informed about the risks associated with different types of investments and understanding market trends can help investors identify red flags and avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
- Additionally, staying engaged with regulatory updates and industry developments can enhance awareness of emerging threats and protective measures.
- Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in preventing fraud by enforcing securities laws and maintaining oversight of financial markets.
- Continued collaboration between regulators, law enforcement, and industry participants is vital to identifying and addressing potential risks.
- Public awareness campaigns and investor education programs can also empower individuals to recognize and report fraudulent activities.
- By fostering a culture of transparency and accountability, the financial sector can reduce the incidence of fraud and create a more secure environment for investors.
Conclusion: The Importance of Vigilance in Financial Practices
- In an ever-evolving financial landscape, the threat of fraud remains a persistent and formidable challenge. The various types of fraud, from Ponzi schemes to insider trading, underscore the need for vigilance and proactive measures to protect investments and maintain market integrity.
- Securities class actions serve as a critical tool in this endeavor, providing a mechanism for investors to seek justice and hold wrongdoers accountable.
- By understanding the dynamics of fraud and the legal recourse available, investors can navigate the complexities of the financial markets with greater confidence and security.
Contact Timothy L. Miles Today for a Free Case Evaluation
If you suffered substantial losses and wish to serve as lead plaintiff in a securities class action, or have questions about securities class action settlements, or just general questions about your rights as a shareholder, please contact attorney Timothy L. Miles of the Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles, at no cost, by calling 855/846-6529 or via e-mail at [email protected]. (24/7/365).
Timothy L. Miles, Esq.
Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles
Tapestry at Brentwood Town Center
300 Centerview Dr. #247
Mailbox #1091
Brentwood,TN 37027
Phone: (855) Tim-MLaw (855-846-6529)
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.classactionlawyertn.com
Facebook Linkedin Pinterest youtube
Visit Our Extensive Investor Hub: Learning for Informed Investors



