Introductionto Strong Internal Controls
Volatile: In today’s volatile financial landscape, investors face unprecedented challenges in maintaining robust portfolios while navigating complex regulatory environments.
Inernal Controls: This playbook serves as your strategic compass, offering battle-tested methodologies to strengthen internal controls and effectively deter securities class actions.
Surge in Securities Class Actions: Recent market turbulence has triggered a 40% increase in securities litigation, making proactive defense mechanisms not just advisable—but essential for portfolio preservation.
A Frameworkk of Strong Internal Contrals Effective internal controls act as your first line of defense against both operational risks and potential legal challenges.
Here’s how to construct an impenetrable system:
Risk Assessment Matrix
- Implement continuous monitoring protocols
- Establish clear escalation pathways for anomalies
- Deploy automated surveillance systems for real-time oversight
Documentation Excellence
Your documentation strategy should be forensically sound and litigation-ready:
- Record all material communications with portfolio companies
- Implement version control for all critical documents
Understanding Securities Class Actions
- Imvestment Landscape: Securities class actions represent a formidable challenge in the financial realm, reflecting the intricate nature of modern investment landscapes.
- Collective Actions: At their core, these lawsuits are collective legal actions initiated by investors who have incurred losses due to alleged corporate misconduct, such as fraud, misrepresentation, or breach of fiduciary duty.
- Remedy: They serve as a mechanism for holding corporations accountable for actions that may have negatively impacted shareholders.
- Proactive: The increasing frequency and complexity of these cases underscore the need for investors to be vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their interests
- Portfolio Destruction: Understanding the dynamics of securities class actions is ccrucial for investors aiming to protect their portfolios from potential legal repercussions.
- Sufficient Markets: The rise of securities class actions can be attributed to several factors, including heightened regulatory scrutiny, evolving legal standards, and the growing sophistication of financial markets.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As the stakes grow higher, companies are often subject to greater scrutiny from regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
- Environmental Securitites Litigation: This environment has led to a surge in litigation, as investors seek recompense for perceived injustices. The complexity of these cases often involves intricate legal and financial evaluations, making it essential for investors to grasp the underlying principles and mechanisms at play.
- Mitigation Exposure: Knowledge of these dynamics helps investors assess risks and develop strategies to mitigate potential exposure to securities litigation.
- Reputational and Financial Damage: Moreover, the impact of securities class actions extends beyond immediate financial losses. The reputational damage to companies involved in securities litigation can be profound, affecting investor confidence and market valuation.
- Due Dilligence: For investors, this translates into a need for due diligence and a keen understanding of the legal landscape.
- Navigating Chal.lenges: By comprehending the intricacies of securities class actions, investors can better navigate the challenges they present, ensuring that they are not caught off guard by the ramifications these lawsuits can entail
- Eovuar Internal Controls: This understanding forms the foundation for implementing robust internal controls that serve as a bulwark against potential legal threats.

The Importance of Internal Controls in Corporate Governance
- Internal controls The backbone of effective corporate governance, acting as safeguards that ensure the integrity of financial reporting and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Transparancy: These controls are essential for Differences In Accounting Periods Fraud: A Manipulative Method to Securities Litigation [2025]: within an organization, thereby protecting shareholder value.
- In the context of securities class actions, robust internal controls can significantly reduce the risk of litigation by preventing errors, fraud, and misconduct that may trigger such lawsuits.
- Securities Class Action: They form a critical component of corporaate governance framework, promoting ethical behavior and sound decision-making.
- Risk Managemen: The significance of internal controls extends beyond mere regulatory compliance. They provide a structured approach to risk management, enabling companies to identify, assess, and mitigate potential threats to their operations and financial health.
- Culture of Accountability:: By implementing comprehensive internal controls, organizations can establish a culture of accountability that permeates all levels of the business.
- Investor Confidence: This culture not only helps deter fraudulent activities but also fosters trust and confidence among investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies.
- Safereguarding Legal Rights: As such, internal controls are indispensable tools for upholding the integrity of corporate governance and safeguarding against legal challenges.
- Corporate Governance: In today’s volatile financial environment, the role of internal controls in corporate governance cannot be overstated. As companies face increasing pressure from investors and regulators to demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices, the need for strong internal controls becomes even more pronounced.
- Transparent Financial Reporting: Controls help ensure that companies adhere to best practices, comply with legal obligations, and maintain transparent financial reporting.
- The Importance of Corporae Governane: understanding the importance of internal controls is crucial for assessing a company’s governance practices and its ability to withstand legal scrutiny.
- Strong Internal Controls: By prioritizing strong internal controls, companies can reinforce their governance structures and minimize the risk of securities class actions.
Internal controls and securities litigation
- Preventive controls: Implementing robust internal controls helps prevent fraud, misstatements, and misconduct by establishing clear procedures, segregating duties, and promoting accountability.
- Deterrence effect: The threat of litigation incentivizes companies to enhance the quality of internal controls and auditors to disclose weaknesses, reducing the likelihood of lawsuits.
- Evidence in lawsuits: Internal control misrepresentations can be sufficient to support securities fraud claims, even without establishing financial misrepresentation.‘
- SEC focus: The SEC actively investigates and brings charges for internal accounting control failures, emphasizing the need for robust internal control regimes.
When internal controls are weak or absent, companies become vulnerable to fraud, which can lead to significant financial losses for investors.
The 2002 Sarbanes-Oxley Act specifically requires public companies to assess and report on the effectiveness of their internal controls over financial reporting, making this a legal obligation, not just a best practice.
How Strong Corporate Governance and Internal Controls Defer Securities Class Action Lawsuits
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) Framework is the gold standard for establishing effective internal controls. It consists of five essential components that work together to prevent financial fraud:
- Control Environment: Sets the foundation through leadership commitment to integrity and ethical values
- Control Activities: Implements policies and procedures that help ensure management directives are carried out
- Information & Communication: Ensures relevant information is identified, captured, and communicated
- Monitoring Activities: Evaluates the quality of internal control performance over time
Companies that properly implement all five COSO components significantly reduce their risk of financial fraud. For example, a strong control environment with clear accountability structures makes it harder for executives to override controls, while effective monitoring activities help detect unusual transactions before they escalate into major fraud.
Key statistics and trends in 2025
- Resolution trends: In the first half of 2025, 121 cases were resolved, with 87 dismissed and 34 settled. This pace suggests a 12% increase in resolved cases compared to 2024.ettlement values:
- The average settlement value increased by 27% to $56 million in the first half of 2025, although the median settlement value decreased by $1.8 million to $12.5 million compared to 2024.
- Litigation risks: Despite a slight decrease in the overall likelihood of facing securities litigation for U.S. exchange-listed companies, the potential financial impact of a lawsuit has increased dramatically.
Emerging litigation areas:
- AI-related claims are on track to exceed 2024 filings, with 13 suits filed in the first six months of 2025.
- Crypto-related filings matched 2024’s total in the first half of 2025.
- The consumer non-cyclical sector saw a 31% increase in filings, primarily driven by biotech and pharma litigation.
- Mega-settlements: There were three settlements over the $1 billion mark by mid-2025, adding to the most extensive set of billion-dollar class action settlements in history.

How Internal Controls Mitigate Legal Risks
Internal controls; Play a vital role in mitigating legal risks by providing a structured approach to managing and monitoring a company’s operations and financial activities.
Establishing Clear Policies and Procedures: Internal controls help ensure that all business transactions are conducted in compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Litigation Reduction Likelihood: This reduces the likelihood of violations that could lead to securities class actions. Moreover, internal controls facilitate accurate financial reporting, which is essential for maintaining transparency and credibility with investors and regulatory authorities.
Mitigating Legal Risks: A key aspect of through iinternal controls is the early detection and prevention of fraudulent activities.
Strong Internal Controls: Include mechanisms for monitoring transactions and identifying irregularities, enabling organizations to address potential issues before they escalate into significant legal challenges.
Financial Losses: This proactive approach not only protects the company from financial losses but also preserves its reputation and credibility in the marketplace.
Minizing Expesure: By effectively managing risks, organizations can minimize their exposure to securities class actions and other legal disputes.
Internal Controls Support Compliance: With corporate governance standards and ethical practices.By promoting a culture of integrity and accountability, internal controls help ensure that employees adhere to the organization’s code of conduct and ethical guidelines.
Ethical Behavor: This commitment to ethical behavior is crucial for maintaining investor trust and confidence, as well as for protecting the company from reputational damage.
Internal Controls and Ethical Practices: By implementing strong internal controls, companies can demonstrate their dedication to ethical practices and reduce the risk of securities class actions arising from misconduct or non-compliance.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND INVESTOR PREVENTAIVE
AND RESPONSE MEASURES
| Preventive Measures | Response Mechanisms |
Corporate | Prevention Mechanisms: • Clear reporting guidelines • Independent board oversight • Robust internal controls • Ethics training & culture | Detection Systems: • Regular external audits • Internal whistleblower systems • Financial statement analysis • Transaction monitoring |
Securities | Red Flags: Falsified Expenses: | Impact on Companies: |
| Stakeholder Actions | Securities Litigation Process: 1. Class action formation 2. Motion to dismiss stage 3. Discovery process 4. Settlement or trial | Investor Protection Steps: |
Investor playbook considerations
- Evaluating internal controls: Investors should assess the quality of a company’s internal controls as a key factor in evaluating potential litigation risk.
- Analyzing risk assessments: Consider whether existing compliance frameworks and controls require updating to address new risks like AI and crypto.
- Due diligence: Thorough research into investments and financial advisors helps investors avoid risky opportunities.
Internal Controls Best Practices
- Segregation of duties: Prevent fraud by ensuring no single individual controls all aspects of a critical business process.
- Periodic reconciliations: Spot discrepancies before they escalate into larger problems.
- Authorization workflows: Establish checkpoints requiring proper business justification before transactions are completed.
- Whistleblower hotline programs: Create a safe space for employees to report concerns about illegal and unethical practices.
- Documentation and evidence standards: Make it harder to create false transactions or manipulate existing ones by requiring supporting documentation for significant transactions.
- Automated controls: Streamline internal control workflows and ensure controls are completed consistently.
- Real-time monitoring: Track issues and anomalies in real-time to identify potential fraud indicators as they occur.
RED FLAGS FOR LACK OF STRONG INTERNAL CONTROLS
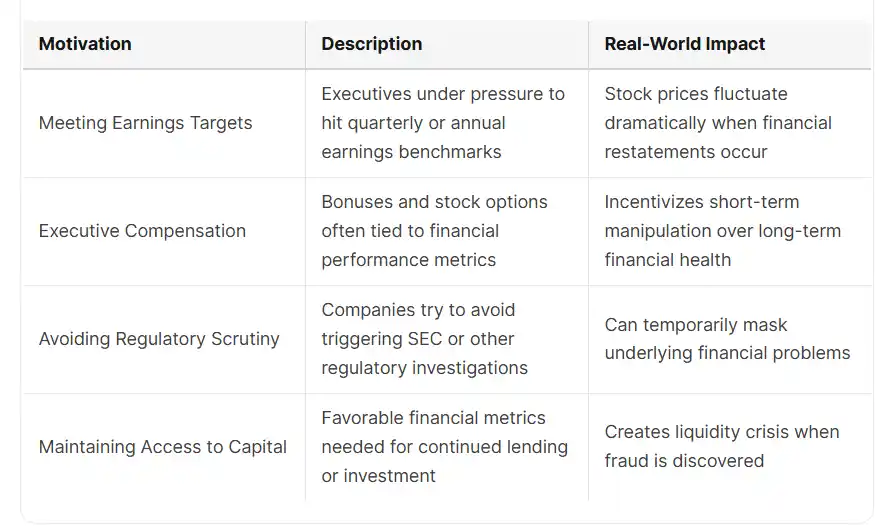
Securities class action lawsuits are typically triggered by significant stock price drops following revelations of potential misconduct in financial reporting. The most common catalysts include:
- Disclosure of material weaknesses in internal controls
- Revelation of accounting irregularities or fraud
- Sudden changes in key accounting policies or estimates
- Abrupt departures of senior financial executives or auditors
- Regulatory investigations by the SEC or other authorities
The Role of Compliance in Preventing Securities Class Actions
- It encompasses the processes and practices that ensure a company adheres to legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies.
- By fostering a culture of compliance, organizations can reduce the risk of securities litigation and protect their reputation and financial stability.
- Effective compliance programs are designed to proactively identify and address potential issues before they lead to costly litigation or regulatory penalties.
- A robust compliance program involves continuous monitoring and assessment of the company’s operations and procedures to identify areas of potential risk.
- This includes regular audits and reviews of financial statements, as well as ongoing training and education for employees on legal and regulatory requirements.
- By providing employees with the knowledge and tools they need to comply with laws and regulations, companies can minimize the risk of inadvertent violations that could lead to securities class actions.
- Furthermore, a strong internal controls program helps establish clear lines of accountability and responsibility, ensuring that all employees understand their roles in maintaining compliance.
- Effective compliance also involves fostering open communication and a strong ethical culture within the organization.
- By encouraging employees to report potential compliance issues or unethical behavior without fear of retaliation, companies can identify and address problems before they escalate into significant legal challenges.
- This commitment to ttransparency and accountability is essential for preventing securities class actions and maintaining investor trust.
- By prioritizing compliance, organizations can protect themselves from legal risks and demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices and corporate responsibility.

Best Practices for Implementing Effective and Strong Internal Controls
- Implementing effective and strong internal controls requires a strategic approach that aligns with the organization’s objectives and risk profile.
- One of the best practices for establishing strong internal controls is to involve all levels of the organization in the process.
- This includes engaging senior management, board members, and employees in the design and implementation of controls.
- By fostering collaboration and communication, companies can ensure that internal controls are comprehensive, relevant, and effective in addressing potential risks.
- Another best practice is to regularly review and update internal controls to ensure they remain effective in a changing business environment.
- This involves conducting periodic assessments of the organization’s control framework to identify areas for improvement and to address emerging risks.
- Companies should also stay informed about changes in regulatory requirements and industry standards to ensure their internal controls remain compliant and up-to-date.
- By maintaining a dynamic and adaptable control environment, organizations can effectively manage risks and protect themselves from securities class actions.
- Technology can be a powerful tool in enhancing internal controls. By leveraging advanced data analytics, automation, and other technological solutions, companies can streamline their control processes and improve the accuracy and efficiency of their risk management efforts.
- Technology can also facilitate real-time monitoring and reporting, enabling organizations to quickly identify and respond to potential issues.
- By integrating technology into their internal control framework, companies can enhance their ability to detect and prevent fraudulent activities and maintain compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Case Studies: Successful and Strong Internal Controls and Class Action Prevention
- Examining case studies of successful internal controls provides valuable insights into how organizations can effectively mitigate the risk of securities class actions.
- One notable example is a multinational corporation that implemented a comprehensive internal control framework to address potential compliance and financial reporting risks.
- By establishing clear policies and procedures, conducting regular audits, and fostering a culture of accountability, the company was able to significantly reduce the incidence of errors and irregularities.
- This proactive approach not only protected the company from legal challenges but also enhanced its reputation and investor confidence.
- Another case study highlights a financial institution that leveraged technology to strengthen its internal controls and prevent securities class actions.
- By implementing advanced data analytics and automated monitoring systems, the institution was able to detect and address potential compliance issues in real time.
- This enabled the organization to quickly identify and mitigate risks, reducing its exposure to securities litigationl
- The use of technology also improved the efficiency and effectiveness of the institution’s risk management efforts, contributing to its overall success in preventing securities class actions.
- A third case study involves a manufacturing company that prioritized employee training and education as part of its internal control strategy.
- By providing employees with comprehensive training on compliance and ethical practices, the company was able to foster a culture of integrity and accountability.
- This commitment to ethical behavior helped prevent incidents of misconduct and fraud, reducing the risk of securities class actions.
- The company’s focus on employee education and engagement also contributed to a positive work environment and strengthened its reputation in the industry.
- For a securities fraud claim to succeed, plaintiffs must establish that the company or its officers made materially false or misleading statements with scienter (intent to deceive), that investors relied on these statements, and that the revelation of truth caused economic losses.
- According to recent data, companies that disclosed material weaknesses in internal controls faced a 29% higher likelihood of securities litigation, with average settlement values 43% higher than other securities class actions.
Core System
- Strong Internal Controls System: The central framework that governs an organization’s risk management approach and financial reporting integrity.
Key Components
- Internal Audit: Independent assurance function that evaluates control effectiveness and identifies improvement opportunities.
- External Audit: Independent third-party verification of financial statements and control assessments as required by securities regulations.
- Management of Internal Controls: Executive responsibility for designing, implementing, and maintaining effective controls.
- Audit Committee: Board-level oversight of financial reporting, strong internal controls, and audit functions.
- Compliance: Monitoring adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies to prevent securities violations.
- Complainant Channel: Whistleblower mechanisms for reporting potential control failures or misconduct.
Securities Litigation Implications
An effective internal control system with all components functioning properly significantly reduces the risk of securities class actions by:
- Preventing material misstatements in financial reporting
- Ensuring timely disclosure of market-relevant information
- Detecting potential fraud or misconduct before it escalates
- Demonstrating the company’s commitment to regulatory compliance
- Creating documentation that can serve as evidence of due diligenc
Frequently Asked Questions About Strong Internal Controls, Securities Litigation and Corporate Governance
What is corporate governance and why is it important in preventing fictitious expenses?
- Corporate governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. It provides the framework for attaining a company’s objectives while balancing the interests of stakeholders including shareholders, management, customers, suppliers, financiers, government, and the community.
- Strong corporate governance is crucial in preventing fictitious expenses because it establishes clear accountability structures and oversight mechanisms. When boards maintain independent audit committees and implement robust reporting channels, the risk of financial manipulation decreases significantly.
- According to recent trends, companies with weak governance structures face a 22% higher likelihood of experiencing financial fraud, with fictitious expenses being among the most common forms.
How does board oversight specifically help prevent financial fraud?
- Board oversight serves as the first line of defense against financial fraud by ensuring management adheres to established policies and procedures. An effective board, particularly through its audit committee, regularly reviews financial statements, questions unusual transactions, and maintains direct communication with both internal and external auditors.
- The board’s responsibility includes establishing a “tone at the top” that emphasizes ethical behavior and transparency. When boards actively engage in financial oversight, they create an environment where fictitious expenses are more likely to be detected and prevented.
- Studies show that companies where boards review expense reports quarterly experience 35% fewer instances of expense fraud compared to those with annual or less frequent reviews.
What are strong internal controls and how do they relate to fictitious expenses?
- Strong Internal controls are the policies, procedures, and organizational structures designed to provide reasonable assurance that company objectives will be achieved and undesired events prevented or detected and corrected.
- The COSO framework outlines five essential components: control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring activities.
- These controls directly prevent fictitious expenses by creating multiple checkpoints where fraudulent transactions can be identified. For example, separation of duties ensures that no single employee can both create and approve an expense, while verification processes confirm that expenses match legitimate business activities.
- Companies with strong internal controls experience up to 60% fewer instances of fraud compared to those with weak or nonexistent controls.
What are the most effective and strong internal controls for preventing expense fraud?
The most effective internal controls for preventing fraud combine technological solutions with clear policies and human oversight. These include:
- Automated approval workflows that require multi-level authorization for expenses above certain thresholds. Digital receipt verification systems that can detect altered or duplicate documentation.
- Regular reconciliation processes that match expenses to supporting documentation and business activities. Clear expense policies with specific guidelines on acceptable expenses and required documentation.
- Additionally, implementing surprise audits has proven particularly effective, as they prevent potential fraudsters from predicting when their activities might be reviewed. Companies that conduct quarterly surprise audits detect fraudulent expenses 40% faster than those relying solely on scheduled reviews.
What role does corporate governance play in preventing securities litigation?
Corporate governance serves as the foundation for preventing securities litigation by establishing the structures through which companies are directed and controlled. Effective governance creates accountability and transparency, significantly reducing litigation risk.
Strong governance includes:
- Independent board oversight that challenges management assertions and financial reporting
- Robust audit committees with financial expertise to detect accounting irregularities
- Clear reporting lines that prevent information silos and ensure transparency
- Recent data shows that companies with weak governance structures face a substantially higher risk of securities litigation.
- Many of these cases stemmed directly from governance failures that allowed financial misreporting to occur.
- When governance breaks down, securities litigation often follows. Courts increasingly scrutinize governance practices when evaluating securities fraud claims, making strong corporate governance not just a best practice but a legal necessity.

How does the lack of strong internal controls lead to securities class actions?
Internal controls over financial reporting are the specific procedures designed to ensure accurate financial statements. When these controls fail, the stage is set for securities litigation through this common sequence:
What are securities class action lawsuits?
Securities class actions are a distinct type of lawsuit filed by investors who have suffered financial losses due to fraudulent activities, misrepresentations, or other violations of securities laws by corporations or their representatives. These legal mechanisms allow multiple investors to collectively pursue claims against defendants, typically corporations and their officers, for alleged violations of federal securities laws.
The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act (PSLRA) provides the regulatory framework governing these actions, establishing specific pleading standards and procedural requirements.

How can companies implement Strong Internal Controls to reduce litigation risk?
- Strong Internal Controls serve as a ccorporation’s first line of defense against potential securities fraud allegations.
- By implementing robust financial reporting protocols, independent audit committees, and comprehensive disclosure review procedures, companies can significantly reduce their exposure to securities litigation
- These controls should include regular financial statement certifications by executives, documented disclosure committee meetings, and systematic risk assessment processes.
- Companies with demonstrably strong internal controls are better positioned to refute allegations of scienter—the intent to deceive, manipulate, or defraud—which is a critical element in securities fraud claims.
What strategies are effective for Deterring Securities Class Actions?
Deterring Securities Class Actions requires a proactive approach to corporate governance and disclosure practices. Effective strategies include:
- Transparent communication: Providing comprehensive, timely, and accurate information to investors about material developments
- Cautious forward-looking statements: Using appropriate safe harbor language when making projections
- Proactive risk disclosure: Identifying and communicating potential risks before they materialize
- Executive training: Educating officers about disclosure obligations and potential liability
- Stock trading policies: Implementing robust insider trading protocols and blackout periods
The role of these deterrence strategies cannot be overstated as they serve as preventive measures against potential allegations of misconduct while promoting market integrity.
How do securities class action lawsuits impact corporate defendants?
Securities class action lawsuits create significant financial and reputational challenges for corporate defendants. Beyond the potential settlement costs, which averaged $75.4 million in 2023 for cases with disclosed amounts, these actions can trigger regulatory investigations, disrupt business operations, and erode investor confidence. The litigation process typically begins with a motion to dismiss phase, where defendants challenge the sufficiency of plaintiffs’ allegations before proceeding to costly discovery. Companies facing these lawsuits must carefully balance their legal defense strategy with business continuity and stakeholder communication concerns.

Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between corporate governance, strong internal controls, and securities litigation is essential for both investors and corporate executives. By recognizing how governance failures and control deficiencies can lead to financial misreporting and subsequent litigation, companies can take proactive steps to mitigate these risks.
If you have questions about securities class actions or believe you may have suffered losses due to corporate
Contact the Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles Today
If you suffered substantial losses in any case and wish to serve as lead plaintiff in the case, or if you just have general questions about you rights as a shareholder, please contact attorney Timothy L. Miles of the Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles, at no cost, by calling 855/846-6529 or via e-mail at [email protected].
For more information on shareholder rights, investor protection, and securities law in general, please visit our Investor Resources Center and our Frequently Asked Questions page with answers to over 350 questions on every area of securities law, civil procedure and much more. Also, please see our Lead Plaintiff Deadline page which has a calendar when lead plaintiff motions are due in various securities cases.
We hope you enjoy, you will find a wealth of information on shareholder rights, protections, and securities law in general.
Timothy L. Miles, Esq.
Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles
Tapestry at Brentwood Town Center
300 Centerview Dr. #247
Mailbox #1091
Brentwood,TN 37027
Phone: (855) Tim-MLaw (855-846-6529)
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.classactionlawyertn.com
Facebook Linkedin Pinterest youtube
Visit Our Extensive Investor Hub: Learning for Informed Investors



