Introduction to Implementing Robust Corporate Governance
- Implementing robust corporate governancee can save you from regulatory scrutiny, fines and securities litigation.
- In today’s increasingly complex regulatory environment, compliance represents far more than a checkbox exercise—it serves as the cornerstone of effective internal controls and robust corporate governance.
- Organizations operating in this landscape face unprecedented scrutiny, where non-compliance can trigger devastating consequences including securities class action lawsuits, substantial financial penalties, and irreparable reputational damage that erodes stakeholder trust for years to come.
Understanding Internal Controls in the Modern Regulatory Framework
- Understanding Internal Controls requires recognizing their dual function as both operational safeguards and compliance mechanisms.
- These systems establish comprehensive frameworks for monitoring and enforcing regulatory requirements across all organizational levels.
- Modern internal control systems must address multiple regulatory domains simultaneously, including financial reporting standards under the Sarbanes-Oxley of 2002, data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA, and industry-specific regulations that vary dramatically across sectors.
The Importance of Segregation of Duties
- The sophistication required in today’s internal control environment cannot be overstated.
- Organizations must implement policies and procedures that ensure every transaction, disclosure, and business decision aligns with applicable legal and regulatory standards.
- This includes establishing robust documentation protocols, implementing segregation of duties, and creating comprehensive audit trails that can withstand regulatory scrutiny and potential litigation challenges.
Corporate Governance and Securities Litigation Risks
- Corporate governance failures frequently serve as the foundation for securities litigation, making the integration of compliance considerations into governance structures absolutely critical.
- When organizations fail to maintain adequate internal controls, they create vulnerabilities that can lead to material misstatements, omissions of critical information, or other violations that trigger securities class actions.
- Recent trends in securities class action lawsuits demonstrate how compliance failures can cascade into significant legal exposure.
- Companies that inadequately disclose risks, fail to implement proper internal controls over financial reporting, or neglect emerging regulatory requirements often find themselves defending against investor claims alleging securities fraud.
Financial Consequences of Failing to Implement Proper Controls
- These cases typically focus on whether organizations maintained adequate systems to ensure accurate and complete disclosures to investors and regulatory bodies.
- The financial impact of such litigation extends far beyond settlement amounts.
- Securities class actions can result in years of costly legal proceedings, regulatory investigations, and ongoing compliance monitoring requirements that strain organizational resources and management attention.
- Moreover, the reputational damage associated with securities litigation can affect customer relationships, employee retention, and access to capital markets.
Proactive Compliance Strategies and Risk Mitigation
- Organizations must adopt proactive approaches to regulatory compliance that anticipate rather than merely react to regulatory changes.
- This requires establishing dedicated compliance teams with clear reporting lines to senior management and board oversight committees.
- These teams must maintain current knowledge of regulatory developments, assess their potential impact on organizational operations, and implement necessary changes to internal control systems before violations occur.
Regular Employee Training
- Regular training and development programs represent essential components of effective compliance strategies. Employees at all levels must understand their roles in maintaining compliance, recognizing potential violations, and escalating concerns through appropriate channels.
- This training must be ongoing, updated regularly to reflect regulatory changes, and tailored to specific roles and responsibilities within the organization.
Collaborating with Experts
- Collaboration with legal and compliance experts provides organizations with specialized knowledge necessary to navigate complex regulatory requirements.
- External advisors can offer objective assessments of compliance programs, identify potential vulnerabilities, and recommend enhancements to internal control systems.
- This collaboration becomes particularly valuable when addressing emerging regulatory areas or industry-specific requirements that require extensive expertise.
Technology Integration and Compliance Monitoring
- Modern compliance programs increasingly rely on technology solutions to enhance monitoring capabilities and ensure consistent application of internal controls.
- Automated systems can flag unusual transactions, monitor compliance with established policies, and generate reports that facilitate regular reviews and audits.
- These technological tools enable organizations to process larger volumes of transactions while maintaining appropriate oversight and control.
- Data analytics and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing compliance monitoring by identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate potential violations.
- These tools can analyze vast amounts of data to detect trends, assess risks, and prioritize areas requiring additional attention.
- However, organizations must ensure that their use of these technologies complies with applicable privacy and data protection regulations.
Building Sustainable Compliance Culture
- Creating a sustainable compliance culture requires commitment from leadership and integration of compliance considerations into all business processes.
- This culture must emphasize transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in compliance practices.
- Organizations that successfully build such cultures typically experience fewer compliance violations, reduced litigation risks, and stronger stakeholder confidence.
The Importance of Independ Assessments
- Regular audits and reviews serve as critical components of effective internal control systems, providing independent assessments of compliance program effectiveness and identifying areas requiring improvement.
- These reviews must be conducted by qualified personnel with appropriate independence and expertise to ensure objective evaluations.
An Integrated Approach
- By prioritizing regulatory compliance and integrating it comprehensively into their internal control systems, organizations can significantly mitigate legal and financial risks while maintaining stakeholder confidence.
- This integrated approach creates sustainable competitive advantages by reducing operational risks, enhancing decision-making processes, and building trust with investors, customers, and regulatory authorities.
- The evolving regulatory landscape will continue presenting new challenges, but organizations with robust, adaptable compliance frameworks will be better positioned to navigate these changes successfully while avoiding the devastating consequences of securities litigation and regulatory violations.
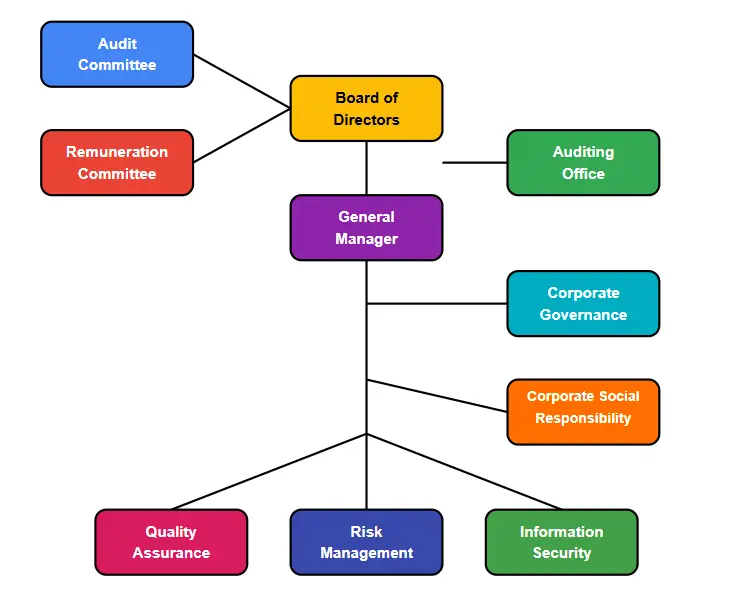
Understanding Corporate Governance: Definition and Importance
- Corporate governance refers to the system by which companies are directed and controlled.
- It encompasses a set of rules, practices, and processes used to balance the interests of a company’s many stakeholders, including shareholders, management, customers, suppliers, financiers, government, and the community.
- The framework ensures that the company is managed in a manner that is accountable and transparent to its stakeholders.
- This concept is essential because it not only provides the blueprint for attaining a company’s objectives but also stipulates the means of attaining and monitoring performance.
Enhanced Reputation and Investor Confidence
- In today’s dynamic business environment, the importance of corporate governance cannot be overstated.
- It plays a critical role in defining the roles and responsibilities of the board of directors, management, and other stakeholders.
- Effective governance structures help in preventing corporate scandals, fraud, and potential civil and criminal liability of the organization.
- It also enhances the reputation of the company, thereby making it more attractive to investors and customers.
- Robust governance is a vital determinant of a company’s sustainability and long-term success, as it ensures that all actions are in line with the ethical standards and legal frameworks governing the industry.
Implementing Robust Corporate Governance: A Strategic Imperative
- Implementing robust corporate governance requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond mere compliance with basic regulatory standards.
- Companies must establish sophisticated oversight mechanisms that address every aspect of their operations, from financial reporting to strategic decision-making processes.
- This implementation involves creating clear accountability structures where board members understand their fiduciary duties and management operates within well-defined parameters.
Monoriting and Evaluating Performance
- The foundation of effective governance lies in establishing strong internal controls that monitor and evaluate company performance continuously.
- These controls serve as early warning systems, identifying potential issues before they escalate into significant problems that could expose the organization to securities litigation.
- Companies that prioritize comprehensive internal control systems demonstrate their commitment to transparency and stakeholder protection.
Mitigating Securities Litigation Risks Through Governance Excellence
- The relationship between corporate governance failures and securities class action lawsuits is undeniable.
- When companies fail to maintain adequate disclosure practices or implement sufficient oversight mechanisms, they become vulnerable to securities class actions filed by investors who have suffered financial losses due to alleged misrepresentations or omissions.
- Securities litigation often stems from governance breakdowns where companies fail to establish proper communication channels between management and the board, or where internal controls prove inadequate to detect material information that should be disclosed to investors.
Reputation Damages
- The financial and reputational costs associated with such securities litigation can be devastating, making prevention through robust governance practices not just advisable but essential.
- Companies facing securities class action lawsuits frequently discover that their governance failures created the very conditions that led to investor harm.
- These cases typically involve allegations that corporate leaders knew or should have known about material information that was not properly disclosed to the market, resulting in inflated stock prices and subsequent investor losses when the truth emerged.
Internal Controls: The Foundation of Corporate Integrity
- Sophisticated internal controls represent the operational backbone of effective corporate governance.
- These systems must be designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting, the effectiveness of operations, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- The implementation of comprehensive internal controls requires significant investment in both technology and human resources.
The Importance of Addressing Advancing Technologies
- Modern internal controls must address the increasing complexity of business operations, including digital transformation initiatives, global supply chains, and evolving cybersecurity threats.
- Companies must regularly assess and update their control systems to ensure they remain effective in identifying and mitigating emerging risks.
- The integration of technology into internal control systems has revolutionized how companies monitor their operations.
- Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence tools now enable real-time monitoring of key risk indicators, allowing companies to identify potential issues before they become material problems that could trigger securities litigation.
Future-Proofing Corporate Governance
- As the business landscape continues to evolve rapidly, companies must adapt their governance practices to address emerging challenges and opportunities.
- The integration of new technologies, changing stakeholder expectations, and evolving regulatory frameworks require governance systems that are both robust and flexible.
- Companies that successfully navigate these challenges will be those that view corporate governance not as a static compliance exercise but as a dynamic strategic advantage that enables sustainable growth and stakeholder value creation.
Key Principles of Robust Corporate Governance
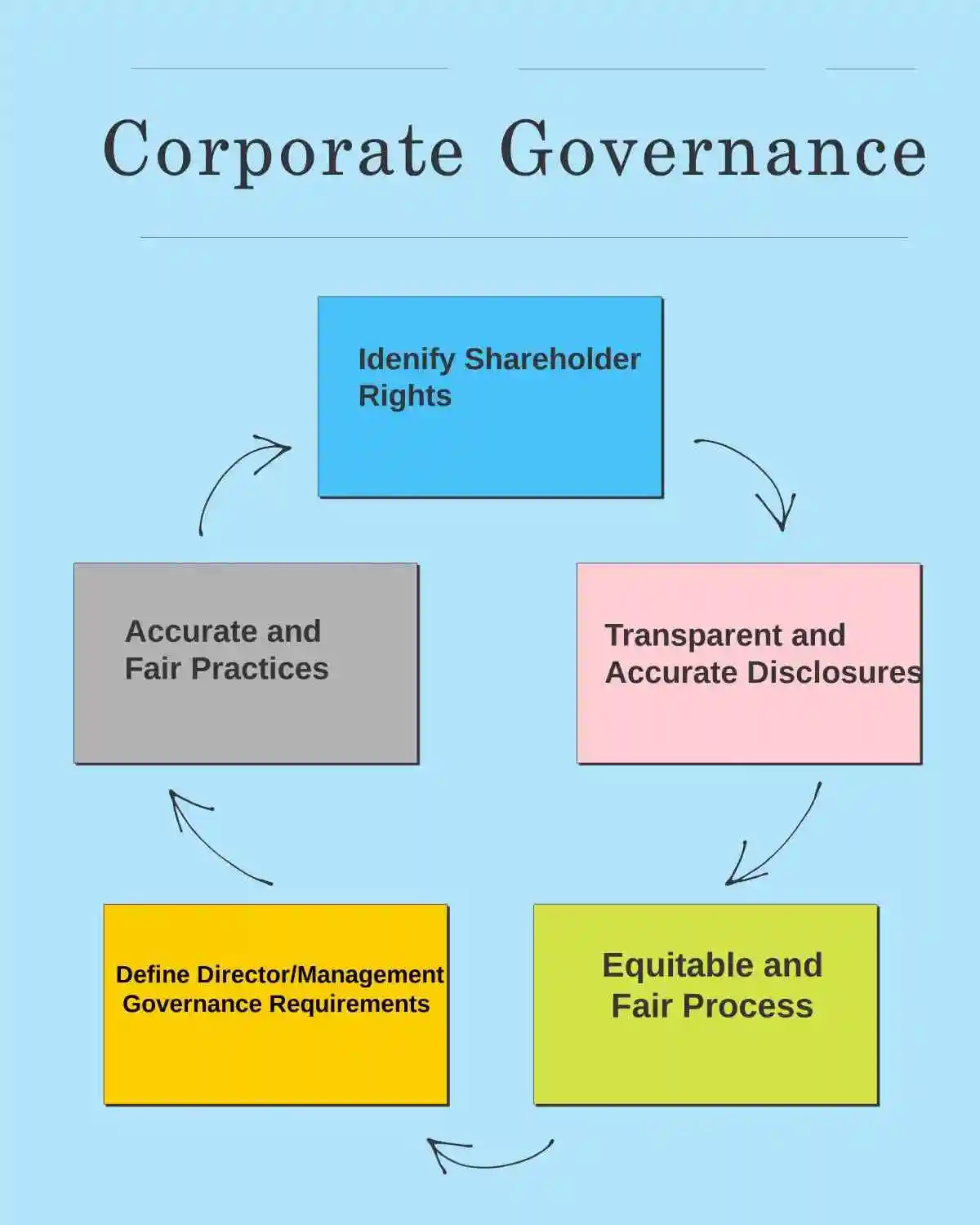
- The foundation of robust corporate governance lies in a set of key principles that guide organizations in maintaining integrity and transparency.
- One of the most critical principles is accountability, which ensures that those in charge of governance are answerable to the stakeholders.
- This involves clear delineation of roles and responsibilities within the organization, making sure that decision-makers are held accountable for their actions and decisions.
Transparency
- Transparency is another pivotal principle, requiring that all pertinent information regarding the corporation’s activities, financial performance, and governance practices are disclosed in a timely and accurate manner.
- This openness allows stakeholders to make informed decisions and builds trust between the company and its stakeholders.
- Furthermore, transparency helps in identifying potential risks and opportunities, enabling the organization to respond proactively.
Fairness and responsibility
- Fairness and responsibility are also core principles that underpin effective corporate governance.
- Fairness involves treating all stakeholders – including minority shareholders – equitably and without bias.
- Responsibility entails that the board of directors and management act in the best interests of the company and its stakeholders, considering the long-term implications of their decisions.
- By adhering to these principles, organizations can establish a governance framework that supports sustainable growth and ethical business conduct.
Implementing Robust Corporate Governance in Practice
- Implementing robust corporate governance requires more than theoretical understanding—it demands systematic execution across all organizational levels.
- Companies must establish comprehensive internal controls that monitor compliance with regulatory requirements and detect potential violations before they escalate into securities litigation.
Strengthening Accountability Mechanisms
- Effective accountability begins with clearly defined roles and reporting structures.
- Board committees must maintain independence from management, particularly audit committees responsible for financial oversight.
- For example, companies facing securities class action lawsuits often exhibit weak board oversight where directors failed to question management’s representations or adequately supervise financial reporting processes.
Key Accountability Measures
- Independent board composition with at least majority independent directors
- Regular executive sessions without management present
- Comprehensive director and officer liability insurance
- Clear whistleblower policies protecting employees who report misconduct
Enhancing Transparency Through Disclosure Excellence
- Transparency extends beyond minimum regulatory compliance to proactive communication with stakeholders.
- Companies must develop robust disclosure controls and procedures that ensure material information reaches the market promptly and accurately.
- The failure to maintain adequate disclosure practices frequently triggers securities class actions when investors suffer losses due to misleading or omitted information.
Integrate Modern Transparancy Protocols
- Modern transparency initiatives encompass:
- Real-time disclosure protocols for material developments
- Comprehensive risk factor disclosures in SEC filings
- Regular investor communications beyond quarterly earnings
- Clear explanations of complex business arrangements or transactions
Implementing Fair Treatment Standards
- Fairness in corporate governance requires systematic protection of minority shareholder rights and equitable treatment across all stakeholder groups.
- Companies must establish policies preventing conflicts of interest and ensuring that related-party transactions receive appropriate scrutiny.
- Securities litigation often arises when controlling shareholders or management extract value at the expense of minority investors.
Essential Fairness Protections Include
- Independent evaluation of related-party transactions
- Equal access to material information for all shareholders Prohibition of selective disclosure practices
- Clear policies governing insider trading and blackout periods
Establishing Responsibility Frameworks
- Corporate responsibility encompasses both legal compliance and ethical decision-making. Directors and officers must understand their fiduciary duties and the potential consequences of governance failures.
- The rise in securities class action lawsuits demonstrates the significant financial and reputational costs of inadequate governance oversight.
Responsibility Frameworks
- Responsibility frameworks shold address:
- Regular director education on evolving regulatory requirements
- Comprehensive risk management systems
- Clear escalation procedures for potential compliance issues
- Regular assessment of governance effectivenessRegulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
- Regulatory compliance forms the backbone of effective corporate governance, requiring organizations to stay current with evolving legal standards.
- The regulatory landscape continues expanding, with new requirements emerging around cybersecurity, environmental disclosure, and artificial intelligence governance.
- Companies must develop adaptive compliance systems that can respond to regulatory changes while maintaining operational efficiency.
Develope Systematic Processes for Identifying Risk
- Internal controls serve as the operational foundation for governance principles, providing systematic processes for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks.
- Effective internal control systems help prevent the material weaknesses and disclosure failures that often precipitate securities litigation.
- These systems must evolve continuously to address emerging business risks and regulatory requirements.
Real-World Implications and Best Practices
- The consequences of governance failures extend far beyond regulatory penalties.
- Companies facing securities class actions often experience significant market capitalization losses, increased regulatory scrutiny, and damaged stakeholder relationships.
- However, organizations that prioritize robust governance frameworks typically demonstrate greater resilience during market volatility and regulatory challenges.
Best Practices for Sustainable Governance
- Best practices for sustainable governance include:
- Regular third-party assessments of governance effectiveness
- Continuous monitoring of peer company practices and regulatory developments
- Integration of governance considerations into strategic planning processes
- Clear communication of governance priorities throughout the organization
Building Long-Term Value Through Governance Excellence
- Robust corporate governance creates sustainable competitive advantages by fostering stakeholder trust, reducing regulatory risk, and enabling more effective strategic decision-making.
- Companies that excel in governance often command premium valuations and experience lower costs of capital, demonstrating the tangible benefits of principled leadership.
- The investment in comprehensive governance systems pays dividends through reduced exposure to securities litigation, enhanced regulatory relationships, and stronger stakeholder confidence.
Focus on Long-Term Sustainability
- As regulatory requirements continue evolving and investor expectations increase, organizations that prioritize governance excellence position themselves for long-term success while protecting against the significant risks associated with governance failures.
- By establishing and maintaining these fundamental principles—accountability, transparency, fairness, and responsibility—organizations create the foundation for sustainable growth, stakeholder trust, and protection against the costly consequences of governance breakdowns that too often result in securities class action lawsuits and regulatory enforcement actions.
The Critical Role of Board Directors in Corporate Governance
- The board of directors serves as the cornerstone of corporate governance, wielding unprecedented influence over a company’s strategic direction, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
- Their responsibilities extend far beyond traditional oversight—they are the primary guardians against securities class action lawsuits that can devastate shareholder value and corporate reputation.
- In today’s complex regulatory environment, boards face mounting pressure to establish comprehensive governance frameworks that satisfy increasingly stringent regulatory requirements.
- The consequences of governance failures have never been more severe, with securities litigation reaching record levels and settlements averaging $$43 million in 2024 alone.
A Look at Securities Class Action Filing Levels
- The number of securities class action filings in 2024 was consistent with long-term historical averages but higher than the previous two years.
- Life sciences companies: These firms saw a significant increase in filings in 2024, reaching 40% above the average from 1997 to 2023.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI-related securities litigation more than doubled in 2024 compared to 2023, with most cases filed in the tech sector.
- SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) and crypto-assets: The number of filings related to these areas declined significantly in 2024.
Factors influencing 2024 outcomes
- Mega-settlements: A lower number of settlements valued at over $100 million in 2024 ($3.7 billion total) contributed to the decline in the average settlement value.
- Lower plaintiff damages: According to Cornerstone Research, a decrease in “plaintiff-style damages” played a key role in the smaller average settlement size.
- Lower institutional investor involvement: With fewer institutional investors acting as lead plaintiffs in 2024, settlement amounts were generally lower.
- More SPAC-related cases: The higher proportion of SPAC settlements, which typically involve lower amounts, further drove down the average.
Broader Impacts of Securities Litigation
- Reputational damage
- Lower stock prices
- Higher legal costs
- Difficulty securing financing
- Negative effects on operating performance
2024 Securities Litigation Filing Trends
- Increase in filings: The total number of securities class action filings increased slightly in 2024 for the second consecutive year. Federal filings were at their highest since 2020, with 229 filed, matching the 2023 total.
- Growth in AI litigation: AI-related securities litigation more than doubled in 2024, driven by factors such as data security incidents, market reactions to missed projections, and issues involving transparency and disclosures.
- Life sciences sector scrutiny: The life sciences industry saw a significant increase in securities filings, with lawsuits reaching 40% above the historical average. This is likely due to the inherent volatility of the sector and the financial impact of events like delayed or failed clinical trials.
- Other key trends: Filings related to COVID-19 increased, while those involving SPACs and cryptocurrency continued to decline. The number of cases filed in the Ninth Circuit exceeded those in the Second Circuit for the second year in a row.


Strategic Oversight and Risk Management Excellence
Robust Disclosure Practices
- Implementing robust corporate governance begins with boards establishing clear accountability structures and comprehensive risk assessment protocols.
- Directors must evaluate potential vulnerabilities that could trigger securities class actions, including inadequate financial reporting, insufficient disclosure practices, and weak internal control systems.
- Modern boards operate in an environment where a single governance misstep can result in catastrophic legal consequences.
- Consider the recent surge in securities class action lawsuits—229 new federal cases were filed in 2024, maintaining the previous year’s elevated levels.
Technology and Healthcare Sectors
- Technology and healthcare sectors accounted for the majority of these filings, highlighting how rapidly evolving industries face heightened scrutiny.
- The board’s risk management responsibilities encompass identifying emerging threats, from cybersecurity vulnerabilities to regulatory changes, and ensuring management implements appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Internal controls must be regularly evaluated and updated to address evolving business risks and regulatory expectations.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Risk Mitigation
- Directors bear ultimate responsibility for ensuring their organizations meet all regulatory compliance obligations.
- This includes overseeing financial reporting accuracy, maintaining transparent communication with stakeholders, and implementing policies that prevent securities law violations.
- The financial impact of governance failures is staggering.
Recent Record Breaking Settlements
- Recent settlements demonstrate the severe consequences of inadequate board oversight:
- Volkswagen’s “Dieselgate” scandal resulted in a $4.3 billion settlement to resolve criminal and civil actions
- Wells Fargo’s fake accounts crisis led to multiple regulatory penalties exceeding $8 billion, including $4.3 to settle crimial and civil charges
- Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica settlement reached $5 billion, the largest privacy-related penalty in history
- These cases underscore how governance breakdowns can trigger massive securities litigation and irreparable reputational damage.
Internal Controls and Financial Reporting Integrity
- Boards must ensure management establishes robust financial reporting systems, maintains accurate records, and provides timely, accurate disclosures to investors and regulators.
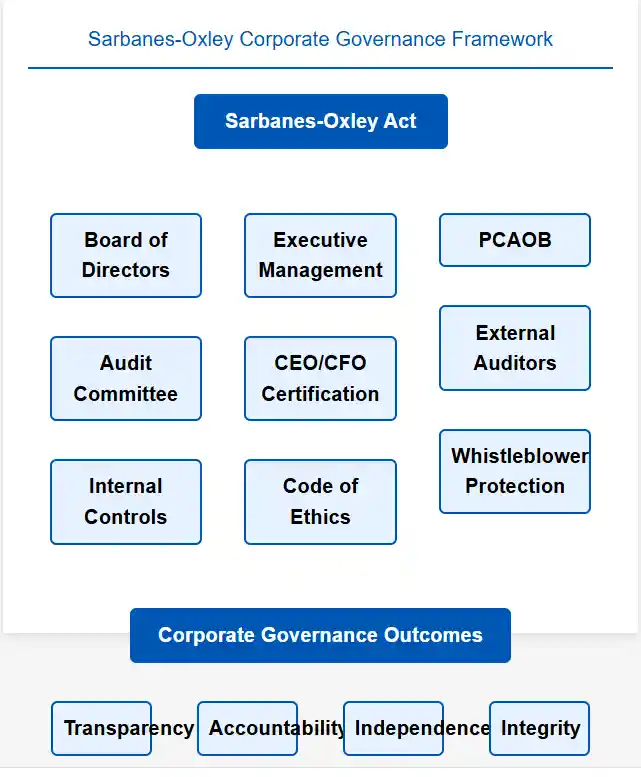
- The Sarbanes-Oxley Act mandates that boards, through their audit committees, oversee internal control effectiveness.
- Directors who fail to fulfill these obligations face personal liability and potential criminal charges.
- Recent enforcement actions demonstrate regulators’ willingness to hold individual directors accountable for governance failures.
- Statistical analysis reveals that companies with strong internal control frameworks experience significantly fewer securities law violations compared to organizations with weak governance structures.
- This correlation highlights the direct relationship between effective board oversight and legal risk reduction.
Executive Leadership and Performance Accountability
- Board directors must establish clear performance metrics for senior executives and regularly evaluate management effectiveness.
- This includes setting compensation structures that align executive incentives with long-term shareholder value creation rather than short-term financial manipulation.
- The board’s role in executive oversight extends to succession planning, ensuring qualified leadership continuity, and maintaining independence from management influence.
Prioritize Directors with Substantial Experience
- Directors must possess the expertise and courage to challenge management decisions that could expose the organization to legal liability.
- Recent trends show that securities class actions increasingly target companies where boards failed to adequately oversee executive conduct.
- Plaintiffs’ attorneys scrutinize board meeting minutes, compensation decisions, and director qualifications when building cases against corporations.
Emerging Governance Challenges and Future Preparedness
- Modern boards face unprecedented challenges from technological disruption, environmental regulations, and evolving stakeholder expectations.
- Directors must stay informed about emerging risks, from artificial intelligence governance to climate change disclosure requirements.
- The regulatory landscape continues evolving rapidly, with new regulatory requirements emerging across multiple jurisdictions.
- Boards must establish processes for monitoring regulatory changes and ensuring timely compliance implementation.
- Companies that proactively address governance challenges demonstrate superior long-term performance and reduced litigation risk.
- Research indicates that organizations with diverse, independent boards experience signicantly fewer regulatory violations and significantly lower settlement costs when legal issues arise.
How Independent Directors Reduce Regulatory Violations
- Enhanced objectivity and oversight. An independent director does not have material or financial relationships with the company’s management. This allows them to monitor management activities and challenge decisions with impartiality, which helps to catch potential compliance issues before they escalate.
- Improved governance and transparency. With diverse professional expertise and an objective perspective, independent directors promote ethical conduct and increase transparency within the organization. This helps build stronger internal controls and better oversight of financial reporting and overall operations, which are key to meeting legal and ethical standards.
- Emphasis on risk management. Effective risk management and compliance are integral functions of an independent board. They can challenge risk assumptions, monitor emerging threats, and ensure that management implements robust strategies to mitigate both internal and external risks.
- Proactive advice and strategic guidance. Independent directors can act as a sounding board and provide strategic advice on compliance requirements, helping management identify potential risks early on. This fosters a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to compliance and helps prevent costly missteps.
How Independent Directors Can Help Lower Settlement Costs
- Reduced litigation risk. Studies suggest that an increase in board independence is associated with a reduction in securities litigation risk. This benefit is especially evident in firms with a higher level of complexity. By proactively addressing issues, an independent board reduces the likelihood of legal actions in the first place.
- Enhanced credibility with stakeholders. Independent directors boost the confidence of investors, regulators, and the public. In the event of a legal issue, a highly credible and independent board can help demonstrate that the company is committed to good governance, potentially leading to more favorable outcomes.
- Better-informed and faster response to crises. In a crisis, independent directors bring an objective perspective and can help the board respond swiftly and decisively. Their unbiased judgment under pressure can help mitigate the impact on a company’s operations, reputation, and financial health.
Building Resilient Governance Frameworks
Creating Comprehensive Policies
- Implementing robust corporate governance requires boards to establish comprehensive policies addressing ethics, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
- Directors must ensure these frameworks evolve with changing business conditions and regulatory expectations.
- Effective governance frameworks include regular board evaluations, continuing education programs for directors, and clear communication channels between the board and management.
- These elements create accountability structures that prevent the governance breakdowns that typically precede securities litigation.
Independend Directors Are more Proactive
- The most successful boards maintain active engagement with legal counsel, regularly review litigation trends affecting their industry, and implement preventive measures before problems emerge.
- This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of facing costly securities class action lawsuits.
- Through diligent oversight, strategic risk management, and unwavering commitment to regulatory compliance, boards of directors can fulfill their fiduciary duties while protecting their organizations from the devastating consequences of securities litigation.
- The investment in robust governance frameworks pays dividends through reduced legal risk, enhanced stakeholder confidence, and sustainable long-term value creation.
Best Practices for Effective Corporate Governance
Diverse Board with Unbiased Oversight
- Implementing best practices in corporate governance is vital to enhancing the effectiveness and resilience of an organization’s governance framework.
- One best practice is the establishment of a well-composed and diverse board of directors. Diversity in terms of skills, experience, gender, and ethnicity can provide varied perspectives and insights, leading to more balanced and informed decision-making processes.
- It is also essential to ensure that a significant portion of the board comprises independent directors who can provide unbiased oversight.
The Importance of Maintaining a Clear Code of Ethics
- Another best practice is the development and maintenance of comprehensive governance policies and procedures, including a clear code of conduct and ethics.
- These policies should be communicated effectively to all employees and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Regular training and awareness programs can help reinforce these governance principles and keep stakeholders informed of any updates or changes.
- Engaging in regular evaluation and review of governance practices is also a critical best practice. This involves conducting periodic assessments of the board’s performance, governance processes, and the effectiveness of risk management systems.
- By identifying areas for improvement and implementing necessary changes, organizations can ensure that their governance practices remain relevant and effective in addressing emerging challenges and opportunities.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Corporate Governance
- Corporate governance is heavily influenced by the legal and regulatory frameworks within which an organization operates.
- These frameworks provide the necessary guidelines and standards that govern the conduct and practices of corporations.
- Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also a critical component of maintaining stakeholder trust and corporate reputation.
Governance Frameworks Must Aligh with Current Laws and Regulations
- In many jurisdictions, corporate governance regulations are enforced by a variety of bodies, including securities commissions, stock exchanges, and government agencies.
- These bodies establish rules regarding financial reporting, disclosure requirements, board composition, and shareholder rights.
- For example, in the United States, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 introduced stringent reforms to improve corporate accountability and prevent financial fraud. Companies listed on stock exchanges must also adhere to specific listing requirements that promote good governance practices.
- Organizations must stay abreast of regulatory changes and ensure that their governance frameworks are aligned with current laws and standards.
- This may involve engaging legal and compliance experts to provide guidance and support in navigating complex regulatory environments.
- By doing so, companies can mitigate legal risks, avoid penalties, and demonstrate their commitment to upholding high standards of governance.
The Impact of Corporate Governance on Business Performance
- Effective corporate governance has a profound impact on a company’s business performance, influencing both financial and non-financial outcomes.
- Strong governance practices enhance decision-making processes, leading to better strategic planning and resource allocation. This, in turn, can result in improved operational efficiency, increased profitability, and sustainable growth.
- Moreover, robust corporate governance can enhance a company’s reputation and brand value, making it more attractive to investors, customers, and business partners.
- Companies with a reputation for strong governance are often perceived as more reliable and trustworthy, which can translate into increased customer loyalty and market share.
Reduced Cost of Capital
- Additionally, good governance practices can reduce the cost of capital by minimizing risks and increasing investor confidence.
- On the non-financial front, effective governance can foster a positive corporate culture that promotes ethical behavior, social responsibility, and environmental sustainability.
- This can lead to increased employee satisfaction, reduced turnover, and a more engaged workforce.
- By aligning governance practices with broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, companies can create value not only for their shareholders but also for the communities in which they operate.
Challenges in Implementing Corporate Governance
- Despite the recognized benefits of corporate governance, many organizations face significant challenges in implementing effective governance frameworks.
- One of the primary challenges is resistance to change, as stakeholders may be reluctant to alter established practices and processes.
- Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership and a clear communication strategy that highlights the long-term benefits of good governance.
The Regulatory Environment
- Another challenge is the complexity of the regulatory environment, which can make it difficult for companies to keep up with regulatory compliance and regulatory requirements.
- This is particularly true for multinational organizations operating in different jurisdictions, each with its own set of rules and requirements.
- Navigating these complexities requires a deep understanding of legal and compliance issues, as well as the ability to adapt governance practices to meet diverse regulatory demands.
- Resource constraints can also pose a significant challenge, especially for smaller organizations that may lack the financial and human resources needed to implement comprehensive governance frameworks.
- These companies may struggle to attract and retain qualified board members and compliance experts, making it difficult to establish and maintain effective corporate governance practices.
- To overcome these challenges, organizations may need to prioritize governance initiatives and seek external support from consultants or advisors to maintain regulatory compliance and avoid securities class action lawsuits.
Tools and Resources for Enhancing Corporate Governance
- To achieve effective corporate governance, organizations can leverage a variety of tools and resources designed to enhance their governance frameworks.
- One valuable resource is governance software, which can streamline board management, facilitate secure communication, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- These platforms often feature tools for document management, meeting scheduling, and performance evaluation, making it easier for boards to operate efficiently and transparently.
- Professional development and training programs are also critical resources for enhancing corporate governance. By providing board members and executives with ongoing education on governance best practices, legal requirements, and emerging trends, organizations can ensure that their leadership is well-equipped to navigate complex governance challenges and meet regulatory requirements.
- Many industry associations and professional bodies offer governance certification programs and workshops that can help build the necessary skills and knowledge.
The Benefit of External Advisors
- Furthermore, organizations can benefit from engaging external advisors and consultants who specialize in corporate governance.
- These experts can provide valuable insights and guidance on designing and implementing effective governance structures, conducting risk assessments, and developing governance policies and procedures.
- By tapping into these resources, companies can enhance their governance practices and ensure alignment with industry standards and regulatory requirements and avoid securities litigation.
Case Studies: Successful Corporate Governance Implementation
Case One
- Examining case studies of successful corporate governance implementation can provide valuable insights and lessons for organizations looking to strengthen their governance frameworks.
- One notable example is the transformation of a global technology company that faced significant governance challenges following a financial scandal.
- By overhauling its board composition, strengthening its risk management processes, and enhancing transparency, the company was able to rebuild stakeholder trust and achieve sustained growth.
Case Two
- Another illustrative case is that of a family-owned business that successfully transitioned to a public company by adopting robust governance practices.
- The company established a diverse and independent board, implemented comprehensive governance policies, and engaged in regular performance evaluations.
- These measures not only facilitated a smooth transition but also contributed to improved financial performance and increased investor confidence.
Case Three
- A third example involves a non-profit organization that achieved remarkable success by integrating corporate governance principles into its operations.
- By establishing clear accountability structures, promoting transparency, and engaging stakeholders in decision-making processes, the organization was able to enhance its credibility, attract new donors, and expand its impact.
- These case studies demonstrate that regardless of size or industry, effective corporate governance can drive positive outcomes and create value for stakeholders.
Conclusion and Future Trends in Corporate Governance
In conclusion, implementing robust corporate governance is a complex but essential endeavor for organizations seeking long-term success and sustainability.
By adhering to key principles, aligning with legal frameworks, and leveraging best practices, companies can enhance their governance structures and foster a culture of integrity and accountability.
This, in turn, can lead to improved business performance, increased stakeholder trust, and sustainable growth.
Contact Timothy L. Miles Today for a Free Case Evaluation
If you suffered substantial losses and wish to serve as lead plaintiff in a securities class action, or have questions about securities class action settlements, or just general questions about your rights as a shareholder, please contact attorney Timothy L. Miles of the Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles, at no cost, by calling 855/846-6529 or via e-mail at [email protected]. (24/7/365).
Timothy L. Miles, Esq.
Law Offices of Timothy L. Miles
Tapestry at Brentwood Town Center
300 Centerview Dr. #247
Mailbox #1091
Brentwood,TN 37027
Phone: (855) Tim-MLaw (855-846-6529)
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.classactionlawyertn.com
Facebook Linkedin Pinterest youtube
Visit Our Extensive Investor Hub: Learning for Informed Investors